Effects of WeChat-based telehealth on patients reported outcomes of hypertension: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40596064
- PMCID: PMC12218959
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04504-4
Effects of WeChat-based telehealth on patients reported outcomes of hypertension: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
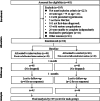
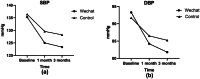
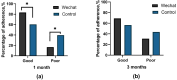
Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) are assessments based on patients' self-perception. This study aimed to explore whether WeChat-based health education is more effective than traditional health education in terms of improving PROs for hypertensive patients during a 3-month period. This prospective, single-center, single-blind randomized controlled trial was conducted from April to August 2022 at the hypertension ward of Yunnan Province Fuwai Cardiovascular Hospital. A total of 96 patients who were aged 18-75 years and diagnosed with primary hypertension for the first time were recruited. The participants were randomly assigned to either the WeChat health education group or the conventional care group at a 1:1 ratio. The intervention lasted for 3 months, with PRO scales administered at baseline (T0), 1 month postintervention (T1), and 3 months postintervention (T2). The experiment ultimately enrolled 96 people, with a mean age of 41 years for the intervention group and 43 years for the control group. Regarding the main outcomes, the total PRO scores of the WeChat group significantly increased from 79.29 points at baseline to 83.68 points after the interventions (95% CI - 7.373, - 1.400; P < 0.05). Additionally, there were significant intergroup differences at 1 month postintervention (TOT: mean difference in change between groups: 3.95, 95% CI 0.127, 7.766, P < 0.05) and at 3 months postintervention (TOT: mean difference in change between groups: 5.05, 95% CI 1.26, 8.833, P < 0.05). This trial demonstrated that WeChat-based telehealth interventions have a positive effect on PROs. The incorporation of digital health education and telehealth interventions can serve as an adjuvant treatment for hypertensive patients.
Keywords: Patients reported outcomes; Primary hypertension; Telehealth education; WeChat-based.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wang, W. N. et al. Experience of stroke survivors and caregivers on self-care: a Meta-synthesis of qualitative research. Chin. J. Nurs.57, 1247–1255 (2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2024RCTJ-XK002/Talent Trusteeship Program of Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
- 2024RCTJ-XK003/Talent Trusteeship Program of Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
- 202401AY070001-067/Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology-Kunming Medical University Applied Basic Research Joint Special Top-level Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

