A graph-based computational approach for modeling physicochemical properties in drug design
- PMID: 40596100
- PMCID: PMC12218534
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06624-3
A graph-based computational approach for modeling physicochemical properties in drug design
Abstract
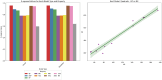
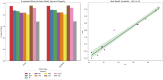
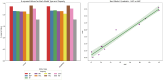
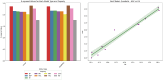
The efficacy and effectiveness of antibiotics and neuropathic drugs are essentially guided by their physicochemical properties governing stability, bioavailability, and therapeutic activity. This work utilises mathematical modelling and quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR) analysis for predicting important physicochemical properties such as boiling point, enthalpy of vaporisation, flash point, and molar refraction of chosen antibiotics and neuropathic drugs. Modified degree-based topological indices are utilised as molecular descriptors for correlations between physicochemical functionality and molecular structure. Linear and quadratic forms are various forms of regression models employed for improved predictions. The findings exhibit excellent performance of quadratic models across all but one property compared to linear models, highlighted by significant statistical markers like high [Formula: see text] values and low error margins. These results highlight the potential use of topological descriptors in combination with sound mathematical frameworks for drug optimisation and early-stage screening.
Keywords: Antibiotic compounds; Molecular graph; QSPR analysis; Regression modeling; Topological indices.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Topological modeling and QSPR based prediction of physicochemical properties of bioactive polyphenols.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 28;15(1):27466. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11863-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40721442 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Quantitative structure property relationship and multiattribute decision analysis of antianginal drugs using topological indices.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 11;15(1):29324. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02473-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40790307 Free PMC article.
-
Topological indices and data analysis techniques modeling to predict the physicochemical properties of tetracycline antibiotics.J Pharm Sci. 2025 Aug;114(8):103871. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2025.103871. Epub 2025 Jun 10. J Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40505728
-
Delayed antibiotics for symptoms and complications of respiratory infections.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD004417. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004417.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD004417. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004417.pub3. PMID: 15495108 Updated.
References
-
- Kanabur, R. & Shigehalli, V. QSPR analysis of degree-based topological indices with physical properties of benzenoid hydrocarbons. Gen. Lett. Math.2(3), 150–169 (2017).
-
- Zaman, S., Yaqoob, H. S. A., Ullah, A. & Sheikh, M. QSPR analysis of some novel drugs used in blood cancer treatment via degree based topological indices and regression models. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd.44(4), 2458–2474 (2024).
-
- Das, P., Mondal, S., Some, B. & Pal, A. Extension of adjacency matrix in QSPR analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst.243(105024), 15–25 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

