Long short-term memory (LSTM) networks for precision prediction of Schottky barrier photodiode behavior at different ıllumination levels
- PMID: 40596142
- PMCID: PMC12215252
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06809-w
Long short-term memory (LSTM) networks for precision prediction of Schottky barrier photodiode behavior at different ıllumination levels
Abstract
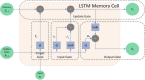
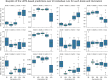
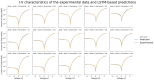
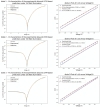
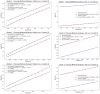
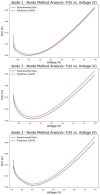
This study has focused on modeling and predicting the electrical properties and parameters of CdZnO interlayered Al/p-Si Schottky Diodes (SDs) using the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) algorithm. The primary aim of this study was to develop a robust predictive model that accurately captures how dopant concentration and illumination levels influence the electrical behavior of SDs. Using the temporal gating and memory capabilities of the LSTM architecture, we proposed a time- and cost-efficient alternative deep-learning model to extensive experimental procedures, ensuring that the diode characterization process could be accelerated without compromising accuracy. The dataset comprises a combination of three Al/CdZnO/p-Si SDs containing different Cd dopant ratios (10%, 20%, and 30%) and five different levels of illumination (50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 mW/cm2). Predictions for electrical parameters, including ideality factor (n), barrier height (FB), and series resistance (Rs), were conducted using the traditional I-V method, Cheung's analysis, and Norde's method. To evaluate the LSTM model predictions, one diode at a specific illumination level was selected as the test set. At the same time, the remaining dataset was divided into 80% for training and 20% for validation. The optimization algorithm was selected as Adaptive Moment Estimation (Adam), and the root mean squared error (RMSE) served as the loss function. Hyperparameters, including the number of epochs (150) and batch size (64), were determined empirically to balance computational efficiency and model performance. Results indicate that predictions on Diode 1 demonstrate strong performance at 50, 100, and 150 mW/cm2 illuminations, exhibiting RMSE values of 11.5, 7.2, and 11 mA, respectively, and R² values exceeding 0.98. LSTM shows on Diode 2 consistently lower errors, achieving a minimum RMSE of 6.22 mA at 100 W (R²=0.993). Diode 3 predictions elevated RMSE and mean absolute error (MAE) at both 50 and 250 mW/cm2. Across Traditional I-V, Cheung's, and Norde's analyses, the LSTM model yields close agreement with experimental measurements, particularly for barrier height and ideality factor. In conclusion, the LSTM model offers a reliable, cost-effective, and time-efficient alternative to exhaustive Schottky diodes experimental measurements. By accurately capturing the nonlinear interplay of doping level and illumination in SDs, this method provides a practical way to expedite device characterization. These findings highlight the potential of data-driven deep learning approaches in semiconductor research and open avenues for broader applications of LSTM architectures in predicting electronic and optoelectronic device parameters.
Keywords: CdZnO thin films; Cheung’s and norde’s method; Illumination effects on I–V characteristics; Long Short-Term memory (LSTM) algorithm; Schottky photodiode.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Does the Presence of Missing Data Affect the Performance of the SORG Machine-learning Algorithm for Patients With Spinal Metastasis? Development of an Internet Application Algorithm.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Jan 1;482(1):143-157. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002706. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 37306629 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Daily standardization of routinely collected milk mid-infrared spectra from dairy herd improvement testing in a statistical framework.J Dairy Sci. 2025 Jul;108(7):7202-7223. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25482. Epub 2025 Apr 28. J Dairy Sci. 2025. PMID: 40306419
References
-
- Azizian-Kalandaragh, Y., Barkhordari, A. & Badali, Y. Support vector machine for prediction of the electronic factors of a Schottky configuration interlaid with pure PVC and doped by Sm2O3 nanoparticles. Adv. Electron. Mater.10.1002/aelm.202400624 (2024).
-
- Hu, Y. et al. Supersensitive, fast-response nanowire sensors by using Schottky contacts. Adv. Mater.22, 3327–3332. 10.1002/adma.201000278 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Kim, S. K., Jeong, S., Kim, J. & Jang, M. Analysis of fermi level pinning characteristics in erbium silicided metal–semiconductor interface. J. Korean Phys. Soc.10.1007/s40042-024-01178-5 (2024).
-
- Wu, C. Y. Interfacial layer theory of the Schottky barrier diodes. J. Appl. Phys.51, 3786–3789. 10.1063/1.328115 (1980).
-
- Al-Hartomy, O. A. et al. Influence of graphite nanosheets on the structure and properties of PVC-based nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci.120, 3628–3634. 10.1002/app.33547 (2011).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

