Combining multi-parametric MRI radiomics features with tumor abnormal protein to construct a machine learning-based predictive model for prostate cancer
- PMID: 40596249
- PMCID: PMC12216994
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05718-2
Combining multi-parametric MRI radiomics features with tumor abnormal protein to construct a machine learning-based predictive model for prostate cancer
Abstract
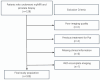
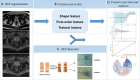
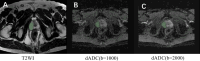
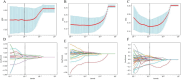
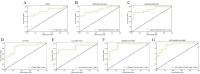
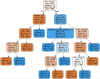
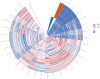
This study aims to investigate the diagnostic value of integrating multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) radiomic features with tumor abnormal protein (TAP) and clinical characteristics for diagnosing prostate cancer. A cohort of 109 patients who underwent both mpMRI and TAP assessments prior to prostate biopsy were enrolled. Radiomic features were meticulously extracted from T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps. Feature selection was performed using t-tests and the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression, followed by model construction using the random forest algorithm. To further enhance the model's accuracy and predictive performance, this study incorporated clinical factors including age, serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, and prostate volume. By integrating these clinical indicators with radiomic features, a more comprehensive and precise predictive model was developed. Finally, the model's performance was quantified by calculating accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, recall, F1 score, and the area under the curve (AUC). From mpMRI sequences of T2WI, dADC(b = 100/1000 s/mm2), and dADC(b = 100/2000 s/mm2), 8, 10, and 13 radiomic features were identified as significantly correlated with prostate cancer, respectively. Random forest models constructed based on these three sets of radiomic features achieved AUCs of 0.83, 0.86, and 0.87, respectively. When integrating all three sets of data to formulate a random forest model, an AUC of 0.84 was obtained. Additionally, a random forest model constructed on TAP and clinical characteristics achieved an AUC of 0.85. Notably, combining mpMRI radiomic features with TAP and clinical characteristics, or integrating dADC (b = 100/2000 s/mm²) sequence with TAP and clinical characteristics to construct random forest models, improved the AUCs to 0.91 and 0.92, respectively. The proposed model, which integrates radiomic features, TAP and clinical characteristics using machine learning, demonstrated high predictive efficiency in diagnosing prostate cancer.
Keywords: Machine learning; Prostate cancer; Radiomics; TAP.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of the second affiliated hospital of Soochow university. Informed consent was obtained from all the patients in the study, and all the procedures were in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures
References
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.71(3), 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Carter, H. B. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening for prostate cancer: revisiting the evidence. Jama319(18), 1866–1868 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

