Biochemical and structural characterization of a reactive intermediate deaminase A homolog from Streptococcus sanguinis
- PMID: 40596262
- PMCID: PMC12218379
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05264-x
Biochemical and structural characterization of a reactive intermediate deaminase A homolog from Streptococcus sanguinis
Abstract
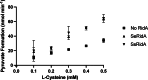
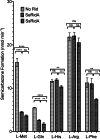
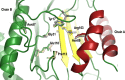
2-Aminoacrylate (2AA) is a short-lived enamine generated as a catalytic intermediate in the dehydration of serine by serine/threonine dehydratase enzymes. 2AA is a metabolic stressor capable of inactivating important pyridoxal phosphate dependent enzymes in a cell. Detoxification of 2AA in a cell is catalyzed by members of the Reactive intermediate deaminase (Rid) family of proteins, which is conserved across all domains of life. We recently identified a RidA homolog, SSA_0809, hereafter SsRidA, in Streptococcus sanguinis with 50% protein sequence identity to a RidA from Salmonella enterica. 2AA deaminase activity assay revealed that SsRidA is capable of enzymatic deamination of 2AA to pyruvate. Furthermore, L-amino acid oxidase assays showed SsRidA has significant activity against several with imino-amino acids similar to the S. enterica RidA. In addition, functional complementation analysis found that SsRidA restored growth of S. enterica ridA mutant in minimal media constituted to increase 2AA stress in the cell. Finally, the crystal structure of SsRidA revealed a homotrimeric protein with active sites at the interface of two interacting monomers. Structure analysis also showed the presence of active site arginine residue along with an active site water molecule implicated in catalysis.
Keywords: Streptococcus sanguinis; 2-Amino acrylate; Enamine deaminase; Metabolic stress; RidA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

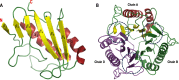
Similar articles
-
Chemical proteomics enhances the understanding of 2AA stress in Salmonella enterica.mSystems. 2025 Jun 17;10(6):e0054025. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00540-25. Epub 2025 May 29. mSystems. 2025. PMID: 40439409 Free PMC article.
-
Perturbation of the MetJ regulon impacts the consequences of 2-aminoacrylate stress in Salmonella enterica.Microbiology (Reading). 2025 Jun;171(6):001572. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001572. Microbiology (Reading). 2025. PMID: 40552973 Free PMC article.
-
Two novel fish paralogs provide insights into the Rid family of imine deaminases active in pre-empting enamine/imine metabolic damage.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 23;10(1):10135. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66663-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32576850 Free PMC article.
-
RidA Proteins Protect against Metabolic Damage by Reactive Intermediates.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020 Jul 15;84(3):e00024-20. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00024-20. Print 2020 Aug 19. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32669283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Morishita, R. et al. Ribonuclease activity of rat liver perchloric acid-soluble protein, a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem.274(29), 20688–20692 (1999). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

