Identification of potential pathogenic genes associated with the comorbidity of rheumatoid arthritis and renal fibrosis using bioinformatics and machine learning
- PMID: 40596265
- PMCID: PMC12216687
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05757-9
Identification of potential pathogenic genes associated with the comorbidity of rheumatoid arthritis and renal fibrosis using bioinformatics and machine learning
Abstract
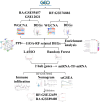
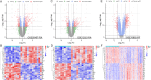
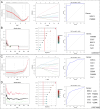
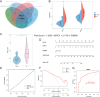
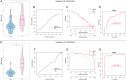
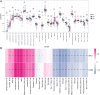
This study aimed to identify the potential pathogenic genes associated with the comorbidity of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and renal fibrosis (RF). Transcriptomic data related to RA and RF were retrieved from the GEO database. Differential expression gene analysis (DEGs) and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) were carried out to identify the RA-RF-DEGs. Subsequently, functional enrichment analysis was performed to clarify the biological functions of these genes. Machine learning algorithms were used to screen for the hub RA-RF differential expression genes, and then a Logistic Regression (LR) model was constructed. The accuracy of the model was evaluated using the ROC curve. At the same time, single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) was applied to conduct immune infiltration analysis on the RF dataset. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was further performed on the hub genes to explore their underlying mechanisms in RF. Finally, a miRNA-TF-mRNA regulatory network centered around the hub genes was constructed.The results showed that 10 RA-RF-DEGs were identified through a comprehensive screening process. Enrichment analysis indicated that these differential expression genes were mainly involved in inflammatory responses and immune regulation. Subsequently, two hub genes, namely BIRC3 and PSMB9, were identified. A LR model was developed, and its predictive accuracy was verified using the ROC curve derived from an external independent dataset. Immune infiltration analysis revealed a significant correlation between the two hub genes and immune dysregulation in RF. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) clarified the potential biological pathways through which BIRC3 and PSMB9 might function in RF. The constructed miRNA-TF-mRNA regulatory network provided a comprehensive overview of the post-transcriptional and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. In conclusion, this study identified two candidate risk genes for RA-RF, providing new insights for the early diagnosis and treatment of RA complicated with RF.
Keywords: Immune infiltration; Machine learning; Renal fibrosis; Rheumatoid arthritis; Risk model.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang, T. et al. Spectrum and prognosis of renal histopathological lesions in 56 Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis with renal involvement. Clin. Exp. Med.20, 191–197. 10.1007/s10238-019-00602-6 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Figus, F. A., Piga, M., Azzolin, I., McConnell, R. & Iagnocco, A. Rheumatoid arthritis: extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun. Rev.20, 102776. 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102776 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Ponticelli, C., Doria, A. & Moroni, G. Renal disorders in rheumatologic diseases: the spectrum is changing (part 2. Arthridides). J. Nephrol.34, 1081–1090. 10.1007/s40620-020-00776-3 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Couderc, M. et al. Prevalence of renal impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from a Cross-Sectional multicenter study. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken)68, 638–644. 10.1002/acr.22713 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

