Utility of the serum alanine aminotransferase to high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in evaluating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis
- PMID: 40596311
- PMCID: PMC12215748
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06171-x
Utility of the serum alanine aminotransferase to high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in evaluating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis
Abstract
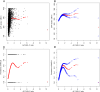
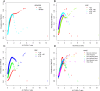
The association of the serum alanine aminotransferase to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio(ALT/HDL-C) with NAFLD remains unclear. This study aimed to examine the association of the ALT/HDL-C ratio with the prevalence of NAFLD and liver fibrosis in the U.S. general population. 4764 participants from the 2017-2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were included in our cross-sectional study. The association of ALT/HDL-C with NAFLD was examined using a general additive model. Furthermore, we conducted subgroup analyses to evaluate the relationship between liver fibrosis, NAFLD risk, and the ALT/HDL-C ratio. Of the 4764 participants, 1513 (31.76%) were diagnosed with NAFLD. All three logistic regression models showed positive associations between NAFLD risk and ALT/HDL-C. Furthermore, in stratified analyses by body mass index (BMI), gender, and age, ALT/HDL-C was positively associated with NAFLD. Hepatic steatosis and fibrosis severity were strongly linked with the ALT/HDL-C. The ALT/HDL-C and the incidence of NAFLD exhibited a nonlinear distribution that was particularly noticeable in women with an inverted U distribution with an inflection point of 0.528. NAFLD was more accurately predicted by ALT/HDL-C than by ALT or HDL-C alone, according to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. A higher ALT/HDL-C ratio in the U.S. population is independently associated with a significantly higher risk of NAFLD and liver fibrosis. The ALT/HDL-C ratio is a useful noninvasive diagnostic tool to quickly and accurately identify those at high risk of developing NAFLD and liver fibrosis.
Keywords: Alanine aminotransferase; Fibrosis; High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; NAFLD; NHANES; Steatosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The National Center for Health Statistics ethics review board approved all NHANES protocols. The participants provided written informed consent to participate in this study. This study uses publicly available secondary data. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Study on the correlation between triglyceride glucose index, triglyceride glucose index to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio, and the risk of diabetes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 23;16:1594548. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1594548. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40626240 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Advanced Fibrosis in the Veterans Health Administration.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Sep;63(9):2259-2266. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5123-3. Epub 2018 May 19. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29779083
-
Association between glycated hemoglobin/high-density lipoprotein ratio and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a U.S. nondiabetic population: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES 2017-2020 data.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 7;25(1):567. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04190-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40775613 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Liver Diseases: NAFLD, NASH, Fibrosis, Cirrhosis-A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 9;14(24):5261. doi: 10.3390/nu14245261. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36558421 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
References
-
- Sheka, A. C. et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A review. Jama323 (12), 1175–1183 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Wu, C. Z. et al. First-phase insulin secretion is positively correlated with Alanine aminotransferase in young adults. Advances in clinical and experimental medicine: official organ. Wroclaw Med. Univ.30 (1), 35–40 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Chen, Q. C. et al. Longitudinal changes in liver aminotransferases predict metabolic syndrome in Chinese patients with nonviral hepatitis. Biomed. Environ. Sci.: BES. 29 (4), 254–266 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2025KY1377/Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province
- 2025KY1377/Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province
- 2025KY1377/Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province
- 2025KY1377/Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province
- 2025KY1377/Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

