Genomic insights into multidrug - resistant Salmonella enterica isolates from pet dogs and cats
- PMID: 40596330
- PMCID: PMC12217845
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06301-5
Genomic insights into multidrug - resistant Salmonella enterica isolates from pet dogs and cats
Abstract
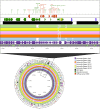
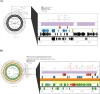
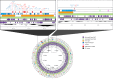
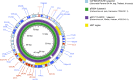
Companion animals are recognized as potential reservoirs and transmitters of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) within the One Health framework. However, in-depth knowledge on AMR in pet animals remains limited. This study aimed to characterize Salmonella from companion dogs and cats using Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS). A total of 25 Salmonella obtained from clinically healthy household dogs and cats were serotyped and had their antimicrobial susceptibility tested. A discrepancy between the serovars identified by traditional slide agglutination tests and those determined by WGS analysis was observed. The isolates exhibited multidrug resistance (MDR) (n = 18) and harbored several resistance genes either chromosomally encoded or plasmid associated. Tn3 and IS26 were commonly found flanking AMR genes and class 1 integrons, while an unusual qacL-IS256-sul3 arrangement was also frequently observed. Similar AMR genes and insertion sequences were found among dogs and cats from different provinces, suggesting clonal spread and horizontal gene transfer of AMR. The similarity between plasmids (i.e., IncX1 and IncI1 plasmid) carrying AMR genes (e.g., aadA1, qacL, sul3, blaTEM-1B, qnrS1, dfrA, tetA) in Salmonella from pets in this study and those from other sources (e.g., humans, food producing animals and environment) in different countries was revealed, suggesting that pet dogs and cats may play a significant role in the global spread of AMR. The finding underscores the role of household pets as silent reservoirs of MDR Salmonella and the need for a One Health approach to tackle the issue. Public health campaigns promoting hygiene practices among pet owners should be encouraged. Pet animals should be incorporated into AMR monitoring and surveillance programs as a component of One Health framework.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
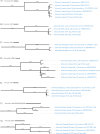
Figures



Similar articles
-
Emergence and characteristics of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Infantis harboring the pESI plasmid in chicken slaughterhouses in South Korea.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0295524. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02955-24. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40454925 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella in pet dogs and cats in Turkey.Vet Med Sci. 2024 Jul;10(4):e1513. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1513. Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38924270 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the genomic and antimicrobial resistance tapestry: comparative insights into Salmonella enterica serotypes Agona, Braenderup, Muenchen, and Panama in Latin American surface waters.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Feb 4;13(2):e0170624. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01706-24. Epub 2024 Dec 13. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39670761 Free PMC article.
-
Nasal Staphylococcus aureus and S. pseudintermedius carriage in healthy dogs and cats: a systematic review of their antibiotic resistance, virulence and genetic lineages of zoonotic relevance.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Dec;133(6):3368-3390. doi: 10.1111/jam.15803. Epub 2022 Sep 27. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36063061 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- IBISWorld. Number of Pets (Cats & Dogs), https://www.ibisworld.com/us/bed/number-of-pets-cats-dogs/75/ (2024).
-
- Review, W. P. Pet Ownership Statistics by Country, https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/pet-ownership-statist... (2024).
-
- International, E. Dog Food in Thailand. (2024).
-
- International, E. Cat Food in Thailand. (2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

