Engineering M13 bacteriophage to display HER2 mimotopes on pVIII for vaccine development
- PMID: 40596331
- PMCID: PMC12219315
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-08032-z
Engineering M13 bacteriophage to display HER2 mimotopes on pVIII for vaccine development
Abstract
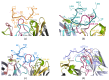
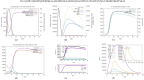
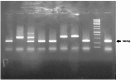
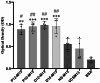
HER2-positive breast cancer is a subtype characterized by overexpression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), which is associated with aggressive tumor growth and poor prognosis. Peptide mimics of HER2 epitopes, recognized by tumor growth-inhibitory antibodies like trastuzumab, have the potential to be developed into effective vaccines. Active immunization with these mimotopes could induce tumor-inhibitory antibodies, offering a cost-effective alternative to trastuzumab therapy. This study aimed to design high-affinity mimotopes to trastuzumab using bioinformatics tools and to evaluate the potential of M13 bacteriophages as platforms for displaying these mimotopes. Using the Peptiderive server, peptide sequences involved in binding HER2 to trastuzumab were identified and refined. Docking studies validated their enhanced binding affinity to trastuzumab. The optimized mimotopes were then displayed on the pVIII coat protein of M13 bacteriophages using the PAK8 phagemid vector. ELISA assays confirmed the binding of these recombinant phages to trastuzumab.This study highlights the effectiveness of using bioinformatics tools to enhance mimotope design for therapeutic applications. The M13 bacteriophage displaying optimized mimotopes shows potential as a vaccine candidate for HER2-positive breast cancer, offering a promising approach to overcoming current limitations of trastuzumab therapy.
Keywords: Bacteriophage; HER2; Mimotope; Phage display; Trastuzumab.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

