Development and validation of a predictive model for continuous renal replacement therapy in sepsis patients using the MIMIC-IV database
- PMID: 40596338
- PMCID: PMC12217637
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-07647-6
Development and validation of a predictive model for continuous renal replacement therapy in sepsis patients using the MIMIC-IV database
Abstract
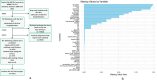
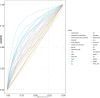
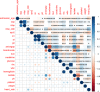
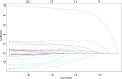
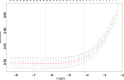
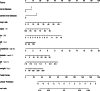
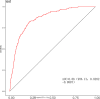
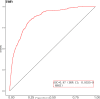
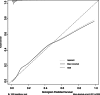
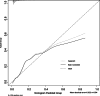
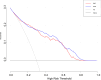
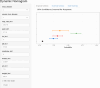
To develop and validate a dynamic nomogram for predicting the need for continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) in septic patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). Data were extracted from the MIMIC-IV 3.0 database and divided into a training set and a validation set in a 7:3 ratio. Relevant risk factors were identified through LASSO regression, and a binary logistic regression model was subsequently developed. The CRRT risk nomogram was visualized using R language, with the DynNom package employed to create a dynamic nomogram. Model performance was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), Harrell's C-index, and calibration curves. The clinical utility of the model was evaluated via decision curve analysis (DCA). A total of 7361 septic patients were included in this study, of which 525 required CRRT. The study identified several predictive factors for CRRT, including respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, international normalized ratio (INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), creatinine, lactate, pH, body weight, renal disease, and severe liver disease. The C-index was 0.871. The AUCs for the training and validation sets were 0.87 (95% CI: 0.8535-0.8883) and 0.86 (95% CI: 0.8282-0.8887), respectively. The calibration curves demonstrated good predictive consistency. DCA confirmed the model's significant clinical value. The dynamic nomogram is available for visualization at: https://zhong-hua-min-zu-wan-sui.shinyapps.io/CRRT_prediction_nomogram/ . We have developed a dynamic nomogram based on the MIMIC-IV database, incorporating 10 clinical features, to predict the probability of CRRT requirement in septic patients. Internal validation showed that this model exhibits robust predictive performance.
Keywords: Continuous renal replacement therapy; Dynamic nomogram; Intensive care unit; Prediction; Sepsis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: Due to the retrospective nature of this study and the de-identified, publicly accessible MIMIC-IV database, the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) waived the requirement for informed consent. Additionally, since the data is de-identified and publicly available, no additional ethical approval is required for the use of MIMIC-IV data in China.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

