Camellia sinensis powder rich in epicatechin and polyphenols attenuates isoprenaline induced cardiac injury by activating the Nrf2 HO1 antioxidant pathway in rats
- PMID: 40596364
- PMCID: PMC12214831
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-08720-w
Camellia sinensis powder rich in epicatechin and polyphenols attenuates isoprenaline induced cardiac injury by activating the Nrf2 HO1 antioxidant pathway in rats
Abstract
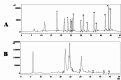
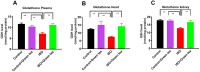
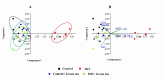
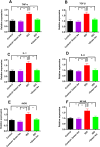
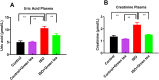
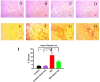
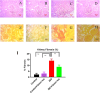
Myocardial infarction is a leading cause of death and morbidity in individuals with cardiovascular diseases. Natural antioxidants, such as those found in green tea leaves, are beneficial in preventing these diseases. This study evaluated the protective effects of green tea leaves powder against isoprenaline (ISO)-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Four groups of male Long Evans rats were used: Control, Control + green tea leaves powder, ISO, and ISO + green tea leaves powder. Organ and blood plasma samples were collected to measure oxidative stress biomarkers, biochemical parameters, and gene expressions. Furthermore, tissue sections were prepared and stained histologically. ISO-induced rats showed decreased cellular antioxidants (catalase activity and glutathione concentration) and elevated oxidative stress markers. Notable inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrosis were observed in the heart and kidneys of ISO-induced rats. Supplementation with green tea leaves powder significantly restored catalase activity and glutathione concentration (p < 0.05) in plasma and tissues. It also considerably reduced lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide, and advanced oxidation protein products (p < 0.05) in ISO-administered rats. Furthermore, green tea leaves powder supplementation halted inflammatory gene expression (p < 0.05), restored antioxidant genes (p < 0.05) such as Nrf-2-HO-1, and prevented cardiac fibrosis in ISO-administered rats. Green tea leaves powder supplementation may reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in ISO-administered rats, potentially through the Nrf-2-HO-1-mediated restoration of antioxidant enzymes and prevention of heart inflammation.
Keywords: Camellia sinensis; Fibrosis; Inflammation; Isoprenaline; Myocardial infarction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

