Black tea rich in polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides inhibits osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice through immune regulation and gut microbiota suppression
- PMID: 40596392
- PMCID: PMC12216683
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-08827-0
Black tea rich in polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides inhibits osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice through immune regulation and gut microbiota suppression
Abstract
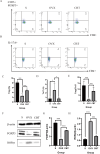
There is a growing interest in identifying dietary strategies to prevent osteoporosis. Black tea has emerged as a potential candidate due to its demonstrated effects on bone metabolism. However, the presence of caffeine in black tea may have an adverse impact on bone health. In our study, we have formulated a compound black tea beverage (CBT) with reduced caffeine content and supplemented with food additives such as Polygonatum polysaccharide. This study aims to investigate alternative mechanisms underlying the anti-osteoporotic effects of this composite black tea preparation. Mice were randomly assigned to sham (S) group, OVX group, and CBT group. After surgery, statistical differences (P < 0.05) became evident when the thermal pain threshold was reached at 5 weeks, while the grip and mechanical pain thresholds were achieved at 6 weeks, persisting until 10 weeks. Following CBT intervention, IL-17 A, TNF-α, TGF-β, β-CTX and PINP levels displayed improvements (P < 0.05). Compared to the OVX mice, CBT mice exhibited varying degrees of improvement in BV/TV, Tb.Th, Tb.N, Tb.Sp (P < 0.05) and a significant decrease in RANKL and TNF-α protein expression in the bone tissue (P < 0.001), along with a significant increase in OPG and TGF-β1 protein expression (P < 0.001). Those treated with CBT exhibited various degrees of improvement in Th17 cells, Treg cells, and the Treg/Th17 cell ratio (P < 0.05) and displayed higher expressions of FOXP3 and lower expressions of ROR-γt in the spleen tissue (P < 0.05). CBT treatment was found to decrease the relative abundance of norank_f_Maurbaculaceae and Lactobacillus, while increasing the relative abundance of Lachnospiraceae NK4A136_group and Dubosella. CBT has been shown to functional behavioral assessments and bone microstructure, thereby effectively retarding the progression of osteoporosis. This impact is postulated to stem from certain bioactive constituents within CBT that act via immune regulation and gut microbiota modulation.
Keywords: Black tea; Gut microbiota; Osteoporosis; Ovariectomized mice; Polygonatum polysaccharide; immune regulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The animal experiments conducted in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, and were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations, including the ARRIVE guidelines. All procedures strictly adhered to the guidelines and regulations set forth by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Experimental Animal Center of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University. The experiments were conducted under the approved protocol number IACUC-202402-16. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent to publish: The authors agree to publication. This manuscript has not been published in any journals.
Figures




References
-
- Li, Z. et al. Dual targeting of bile acid receptor-1 (TGR5) and farnesoid X receptor (FXR) prevents Estrogen-Dependent bone loss in mice. J. Bone Min. Res.34 (4), 765–776 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No.: 2023ZL429/Zhejiang Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Program Project
- No.: 82304760/The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No.: Y202044448/General scientific research projects of Zhejiang Provincial Department of Education
- No.: 2017R410007/Zhejiang Province College Student Science and Technology Innovation Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

