Synergistic effect of Co3O4/CdAl2O4 nanocomposite for photocatalytic decontamination of organic dyes under visible light irradiation
- PMID: 40596534
- PMCID: PMC12215255
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-07095-2
Synergistic effect of Co3O4/CdAl2O4 nanocomposite for photocatalytic decontamination of organic dyes under visible light irradiation
Abstract
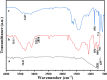
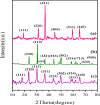
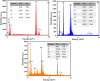
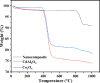
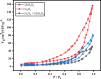
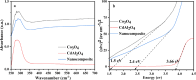
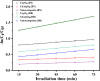
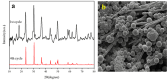
Water supply and the removal of contaminants are critical challenges for modern societies. Various techniques have been developed to treat industrial wastewater. This study synthesized a Co3O4/CdAl2O4 nanocomposite using a hydrothermal method to remove Direct Blue and Basic Yellow organic dyes from aqueous media. The nanocomposite was characterized through FTIR, XRD, FESEM, EDX, TEM, PL, and UV-DRS spectroscopy to assess its physical, chemical, and optical properties, including morphology, particle size, crystalline structure, chemical composition, and band gap. DRS analysis revealed that the band gaps of Co3O4, CdAl2O4, and the synthesized nanocomposite were 1.5 eV, 3.66 eV, and 2.4 eV respectively. The formation of the heterogeneous Co3O4/CdAl2O4 structure reduced the recombination rate compared to pure Co3O4 and CdAl2O4 samples. The study examined how operational parameters such as pH, contact time, initial dye concentration, and catalyst dosage affected dye removal efficiency. Optimal removal efficiency for Direct Blue was achieved at pH 2 and for Basic Yellow at pH 12 with a dye concentration of 10 ppm in a 20 mL solution using a catalyst dosage of 0.01 g. Maximum removal efficiencies were 91% for Direct Blue and 86% for Basic Yellow. Kinetic studies showed that the dye removal process followed pseudo-first-order kinetics indicative of a surface-controlled reaction. The experimental data fit well with this model, allowing calculation of the reaction rate constant and activation energy determination. The regression coefficients were 0.992 for Direct Blue and 0.991 for Basic Yellow with rate constants of 0.00379 s- 1 and 0.00125 s- 1 respectively. The photocatalytic regeneration results indicate that the synthesized nanocomposite demonstrates excellent reusability for up to four cycles, achieving final degradation rates of 80% and 74% for Direct Blue and Basic Yellow, respectively. Mechanistic studies reveal that superoxide radicals are the primary reactive species, serving as powerful oxidants that break down the chemical bonds of pollutant molecules. This process results in bond cleavage and ultimately mineralizes pollutants into simpler compounds like water and carbon dioxide. Consequently, the cobalt oxide/cadmium alumina nanocomposite, with its superior photocatalytic properties and high stability, shows significant potential for treating industrial wastewater containing organic dyes.
Keywords: Basic yellow 28; Cadmium alumina; Cobalt oxide; Direct blue 199; Nanocomposite.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Yousefi, S. R., Alshamsi, H. A., Amiri, O. & Salavati-Niasari, M. Synthesis, characterization and application of Co/Co3O4 nanocomposites as an effective photocatalyst for discoloration of organic dye contaminants in wastewater and antibacterial properties. J. Mol. Liq.337, 116405 (2021). - DOI
-
- Heidari-Asil, S. A. et al. Magnetically recyclable ZnCo2O4/Co3O4 nano-photocatalyst: green combustion preparation, characterization and its application for enhanced degradation of contaminated water under sunlight. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 47, 16852–16861 (2022). - DOI
-
- Hegazy, S., Abdelwahab, N. A., Ramadan, A. M. & Mohamed, S. K. Magnetic Fe3O4-grafted cellulose/graphene oxide nanocomposite for methylene blue removal from aqueous solutions: synthesis and characterization. Next Mater.3, 100064 (2024). - DOI
-
- Ayazi, S., Ghorbani, M. & Abedini, R. Multifunctional composite membranes incorporated by SiO2@ CuFe2O4 nanocomposite for high dye removal, antibacterial and antifouling properties. Chem. Eng. Res. Des.169, 214–228 (2021). - DOI
-
- Falah, S., Ghorbani, M. & Ahmadpour, J. Photocatalytic degradation of anionic and cationic dyes over PPy/CuFe2O4 nanocomposite under visible-light and bactericidal action. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng.144, 104767 (2023). - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

