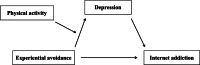
Physical activity moderates the mediating role of depression between experiential avoidance and Internet addiction
- PMID: 40596572
- PMCID: PMC12217329
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-07487-4
Physical activity moderates the mediating role of depression between experiential avoidance and Internet addiction
Abstract
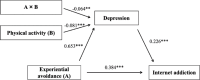
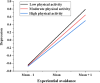
Experiential avoidance is highly correlated with Internet addiction among college students, but the underlying mechanisms between these variables require further exploration. This study aims to elucidate the psychological mechanisms linking experiential avoidance and Internet addiction by examining depression as a mediating factor and physical activity as a moderating factor. A self-report survey was conducted among 1,506 college students from Chinese universities. The survey included measures of experiential avoidance, Internet addiction, depression, and physical activity. Descriptive and correlational analyses were performed on these variables, and a moderated mediation model was constructed. Experiential avoidance showed significant positive correlations with both Internet addiction and depression among college students, while physical activity was significantly negatively correlated with these variables. Depression partially mediated the relationship between experiential avoidance and Internet addiction, and physical activity moderated the relationship between experiential avoidance and depression. This study further clarifies the psychological mechanisms underlying the relationship between experiential avoidance and Internet addiction among college students. Depression serves as a mediator in this relationship, whereas physical activity can attenuate the strength of the relationship between experiential avoidance and depression. These findings underscore the potential of incorporating physical activity into mental health interventions, offering a dual approach to alleviate depression and reduce Internet addiction risk among college students. Moreover, this research provides actionable insights for policymakers and practitioners in designing strategies that promote both psychological well-being and healthy behaviors.
Keywords: College students; Depression; Experiential avoidance; Internet addiction; Physical activity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Biomedicine Ethics Committee of Jishou University before the initiation of the project (Grant number: JSDX-2024-0086). And informed consent was obtained from the participants before starting the program.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Relationship Between Empirical Avoidance, Anxiety, Difficulty Describing Feelings and Internet Addiction Among College Students: A Moderated Mediation Model.J Genet Psychol. 2025 Jul-Aug;186(4):288-304. doi: 10.1080/00221325.2025.2453705. Epub 2025 Jan 21. J Genet Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39836109
-
Social media addiction as the central mediating variable to explore the mechanism between physical exercise and sleep quality.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 23;15(1):26800. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11225-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40702132 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the relationship between physical activity and social media addiction among adolescents through a moderated mediation model.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22209. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05173-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594419 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computer and other electronic aids for smoking cessation: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(38):1-205, iii-v. doi: 10.3310/hta16380. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 23046909
Cited by
-
To explore the relationship between physical activity and sleep quality of college students based on the mediating effect of stress and subjective well-being.BMC Psychol. 2025 Aug 18;13(1):932. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-03303-w. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40826439 Free PMC article.
-
A chain mediation model for physical exercise and sleep quality.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 20;15(1):30527. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16017-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40836074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peng, C. et al. Sex differences in association between internet addiction and aggression among adolescents aged 12 to 18 in Mainland of China. J. Affect. Disord.312, 198–207 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Meng, S. Q. et al. Global prevalence of digital addiction in general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev.92, 102128 (2022). - PubMed
-
- China Internet Network Information Center. The 53rd Statistical Report on the Development of the Internet in China. https://www.cnnic.cn/NMediaFile/2024/0325/MAIN1711355296414FIQ9XKZV63.pdf (2024).
-
- Yan, Q. et al. Trends in the prevalence of internet addiction among adolescents from 2004 to 2019 in Shanghai. Chin. J. School Health. 43 (08), 1193–1197 (2022).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical