CD55 may be a new target for colorectal cancer treatment
- PMID: 40596619
- PMCID: PMC12216819
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-08491-4
CD55 may be a new target for colorectal cancer treatment
Abstract
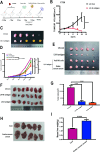
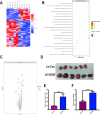
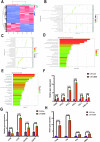
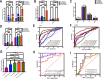
In the early stage, our research group injected lentivirus carrying blood type A antigen into tumors as a drug, and the tumor volume of mice was significantly reduced. We speculate that the complement system plays an important role in anti-tumor therapy, but the specific components are unknown. A mouse model containing blood type antibodies was established. After the mouse axilla formed tumors, lentivirus carrying different blood type antigens was used for treatment. On this basis, NK cell activity was inhibited and the complement system of the body was eliminated. Tumor formation was observed. Flow cytometry was used to observe the changes in tumor tissue and peripheral blood immune cells. Immunohistochemistry was used to observe NK cells in tumors. Proteomics was used to screen differential complement components. Transcriptomics was used to observe the gene expression differences of CT26 cells overexpressing CD55, and RT-PCR was used for verification. The changes of CEA, CA199, CA125, CA153, D-D dimer, total white blood cell count, neutrophil ratio, lymphocyte ratio, monocyte ratio, and fibrinogen in the simple colorectal cancer group, simple liver metastasis group, simple lung metastasis group, and multiple organ metastasis group were retrospectively analyzed, and ROC curves were used for evaluation; ELISA method was used to detect the changes in CD55 content in the healthy group, simple colorectal cancer group, simple liver metastasis group, simple lung metastasis group, and multiple organ metastasis group, and ROC curves were used to evaluate its clinical diagnostic ability. CCK8 and EdU methods were used to detect cell proliferation. Scratch assay and transwell assay were used to observe cell migration. Western blotting was used to observe the changes of MMP9, Vimentin and α-SMA. After the lentivirus carrying blood type A antigen was injected into the axillary tumor of mice, the tumor volume was significantly reduced compared with the control group. The proportion of NK cells in tumor tissue increased significantly. Using antibodies to block NK cell surface activation receptors and eliminate the complement system, both treatments reduced the therapeutic effect. Both blood type B and Rh blood type antigens can significantly reduce tumor volume. Eliminating complement in the body increases the incidence of liver metastasis. The proliferation degree of overexpressed CD55 in tumors is significantly increased. CD55 overexpression can significantly increase the expression of CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL7, CXCL12, TLR7, CSFR1, TCAM, TNF, BTK and MMP9. CEA and CA199 are of certain value in judging liver metastasis, and CD55 has better diagnostic efficacy. Complement significantly inhibits cell proliferation. CD55 significantly promotes CT26 proliferation and migration ability. CD55 is a potential tumor promoter and diagnostic marker for colorectal cancer.
Keywords: ABO blood type; CD55; Colorectal cancer; Complement system; Tumor marker.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Chifeng Hospital(Ethics number: DW2022002 and CK2020004). For the collection of clinical samples, this study strictly adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki, and all individuals participating in the study obtained informed consent and agreed to the publication of the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oncolytic reovirus enhances the effect of CEA immunotherapy when combined with PD1-PDL1 inhibitor in a colorectal cancer model.Immunotherapy. 2025 Apr;17(6):425-435. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2501926. Epub 2025 May 12. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40353308
-
Caveolin-1 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via EGFR degradation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05259-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594106 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Expression of WNT10A in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its effect on cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Mar 28;50(3):402-415. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2025.240237. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40628509 Chinese, English.
-
Levetiracetam add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy: an updated Cochrane Review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD001901. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001901.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972056 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- No:202204010038/Scientific researchproject of Hunan Provincial Health Commission
- No: YKD2022LH072/Inner Mongolia Medical University Joint Project
- No:2024GLIH0990/Public Hospital Research Joint Fund Science and Technology Project
- No: 2021MS08060/Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

