Muscle-Driven prognostication in gastric cancer: A multicenter deep learning framework integrating Iliopsoas and erector spinae radiomics for 5-Year survival prediction
- PMID: 40596621
- PMCID: PMC12215766
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-09083-y
Muscle-Driven prognostication in gastric cancer: A multicenter deep learning framework integrating Iliopsoas and erector spinae radiomics for 5-Year survival prediction
Abstract
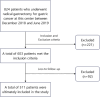
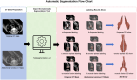
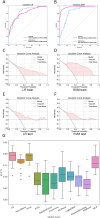
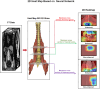
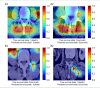
This study developed a 5-year survival prediction model for gastric cancer patients by combining radiomics and deep learning, focusing on CT-based 2D and 3D features of the iliopsoas and erector spinae muscles. Retrospective data from 705 patients across two centers were analyzed, with clinical variables assessed via Cox regression and radiomic features extracted using deep learning. The 2D model outperformed the 3D approach, leading to feature fusion across five dimensions, optimized via logistic regression. Results showed no significant association between clinical baseline characteristics and survival, but the 2D model demonstrated strong prognostic performance (AUC ~ 0.8), with attention heatmaps emphasizing spinal muscle regions. The 3D model underperformed due to irrelevant data. The final integrated model achieved stable predictive accuracy, confirming the link between muscle mass and survival. This approach advances precision medicine by enabling personalized prognosis and exploring 3D imaging feasibility, offering insights for gastric cancer research.
Keywords: Deep learning; Gastric cancer; Radical gastrectomy; Sarcopenia.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no potential conflict of interest in the research, writing, and publication of this article. Financial support: This study was supported by a grant from the Graduate Student Research and Practice Innovation Program of Anhui Medical University (YJS20230080), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82403333).
Figures



References
-
- Fukuda, Y. et al. Sarcopenia is associated with severe postoperative complications in elderly gastric cancer patients undergoing gastrectomy. Gastric Cancer. 19 (3), 986–993. 10.1007/s10120-015-0546-4 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Ricciardolo, A. A. et al. Strong impact of sarcopenia as a risk factor of survival in resected gastric cancer patients: first Italian report of a bicentric study. Updates Surg.74 (1), 283–293. 10.1007/s13304-021-01175-4 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Yang, W. et al. Quantifying skeletal muscle wasting during chemoradiotherapy with Jacobian calculations for the prediction of survival and toxicity in patients with gastric cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol.46 (7), 1254–1261. 10.1016/j.ejso.2020.03.223 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

