Determination of phytochemical content, antioxidant and mineral properties of Astragalus chamaephaca Freyn in different solvents
- PMID: 40596641
- PMCID: PMC12215957
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-95203-7
Determination of phytochemical content, antioxidant and mineral properties of Astragalus chamaephaca Freyn in different solvents
Abstract
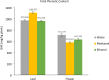
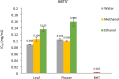
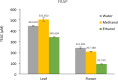
Astragalus species, members of the Fabaceae family, have been used in traditional medicine for centuries. In addition to their traditional applications, many subspecies are now utilized in modern medicine. This study investigated the antioxidative, phenolic, and mineralogical properties of Astragalus chamaephaca Freyn for the first time. Antioxidant capacities were evaluated using the ABTS+ free cation radical scavenging activity, FRAP, and DPPH methods. The total phenolic content was determined using the Folin-Ciocalteu method, while quantification was performed via the LC-MS method. Substantial phenolic compounds, such as p-coumaric acid, gallic acid, rutin, quercetin, and naringenin-known for their diverse biological activities-were identified. In addition, mineralogical analyses have shown the presence of essential elements, such as Ca, Mg, and K, which play crucial roles in human health.
Keywords: Astragalus; p-coumaric acid; Antioxidant activity; Mineralogical properties; Phenolic content.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- VeliogluY.S. & G. Mazza, L. Gao, B.D. Oomah Antioxidant activity and total phenolics in selected fruits, vegetables, and grain products. J. Agric. Food Chem.46, 4113–4117. 10.1021/jf9801973 (1998).
-
- Poswal, F. S. et al. Herbal teas and their health benefits: A scoping review, plant foods Hum. Nutr74, 266–276. 10.1007/s11130-019-00750-w (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

