Experimental investigation on partial cement replacement with binary blended bagasse ash and calcined dolomite for enhanced C-25 grade concrete performance
- PMID: 40596688
- PMCID: PMC12216261
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98019-7
Experimental investigation on partial cement replacement with binary blended bagasse ash and calcined dolomite for enhanced C-25 grade concrete performance
Abstract
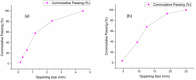
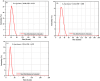
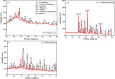
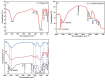
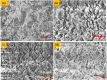
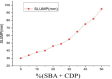
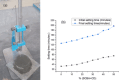
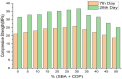
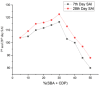
Cement is a globally produced building material and a crucial component of every construction project. Alternative materials, mostly agro-industrial wastes, are emerging as potential cement replacements due to high carbon dioxide emissions associated with cement manufacturing and rising cost of cement. Numerous naturally occurring materials like rice husk ash, corn cob ash, fly ash, slag, silica fume, bagasse ash (BA), and natural pozzolans are used as partial substituents for cement in concrete and mortars due to their strength, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits. BA is frequently used as a partial cement replacement in concrete, but most studies limit its utilization to 15%, highlighting the limitations of pozzolanic materials. This study investigates the effects of binary blended BA and calcined dolomite powder (CDP) as partial cement replacement, i.e., 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, and 50%, on the compressive strength of C-25 grade concrete. Additionally, the physicochemical properties of BA, CDP, and the binary mixture were studied using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Furthermore, the effects of the binary mixture on workability, setting time, compressive strength, strength activity index (SAI), water absorption, and dry density on the concrete were evaluated in detail. The compressive strength was examined by casting 66 standard cubes of 15 cm [Formula: see text] 15 cm [Formula: see text] 15 cm size and curing them for 7 and 28 days. The compressive strength test indicates that by reducing pozzolana particle size below cement grade and blending BA with CDP, up to 30% of cement can be replaced by enhancing the compressive strength to 36.7 MPa at the end of 28 days.
Keywords: Bagasse ash; C-25 grade concrete; Calcined dolomite; Compressive strength; Partial replacement; Pazzolona.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Optimization of Na2O and Activator modulus to produce sustainable ground pond ash and GGBS-based geopolymer concrete.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 Jun;32(26):15975-15994. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36652-5. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40542988
-
Impact of propylene fibers and industrial wastewater on the properties of self-compacting concrete.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 9;15(1):29201. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13454-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40783418 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Predicting the mechanical performance of industrial waste incorporated sustainable concrete using hybrid machine learning modeling and parametric analyses.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 20;15(1):26330. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11601-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40685423 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the behaviour and performance of ashes of agricultural wastes for cleaner production in building materials: a systematic review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 Jun;32(27):16022-16050. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36674-z. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40571790 Review.
References
-
- Fadi Althoey, W. S. A., Muhammad Sufian, A. F. & Deifalla. Advancements in low-carbon concrete as a construction material for the sustainable built environment developments. Built Environ.16, 100284. 10.1016/j.dibe.2023.100284 (2023).
-
- Jing He, S. K. V. A. The utilization of agricultural waste as Agro-Cement in concrete: A review. Sustainability12, 6971. 10.3390/su12176971 (2020).
-
- Yasong Zhao, J. G., Liu, C. & Chen, X. The particle-size effect of waste clay brick powder on its pozzolanic activity and properties of blended cement. J. Clean. Prod.242, 118521. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118521 (2020).
-
- Oluwafemi, E., Ige, O. A. O., Kevin, J., Duffy & Collins, O. C. Environmental impact analysis of Portland cement (CEM1) using the midpoint method. Energies15, 2708. 10.3390/en15072708 (2022).
Grants and funding
- ET2023SIN384A104/ASSURE SI project of general financial framework for VLIR-UOS-funded projects
- ET2023SIN384A104/ASSURE SI project of general financial framework for VLIR-UOS-funded projects
- ET2023SIN384A104/ASSURE SI project of general financial framework for VLIR-UOS-funded projects
- ET2023SIN384A104/ASSURE SI project of general financial framework for VLIR-UOS-funded projects
- ET2023SIN384A104/ASSURE SI project of general financial framework for VLIR-UOS-funded projects
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

