A role of pigment epithelium-derived factor in zinc-mediated mechanism of neurodegeneration in glaucoma
- PMID: 40596696
- PMCID: PMC12215840
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08370-8
A role of pigment epithelium-derived factor in zinc-mediated mechanism of neurodegeneration in glaucoma
Abstract
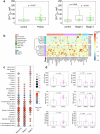
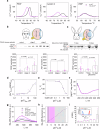
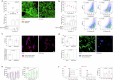
Glaucoma is a neurodegenerative condition involving optic nerve damage and retinal ganglion cells death. Animal studies suggested that the pathway linking these events can be mediated by mobile zinc secreted into the intraretinal space and exerting cytotoxic effects. Whether this mechanism is relevant for human glaucoma and what are the targets of extracellular zinc is unknown. We report that increased zinc content in the aqueous humor and retina is indeed a characteristic of glaucomatous neuropathy, and excess extracellular zinc may be recognized by the key retinal neurotrophic factor PEDF. Biophysical and X-ray crystallographic studies show that PEDF coordinates zinc ions in five types of intermolecular high-affinity sites, leading to a decrease in negative surface charge and reversible oligomerization of the protein, thereby masking the target recognition sites responsible for its neurotrophic and antiangiogenic activities and collagen binding. Notably, PEDF secretion is enhanced in both glaucoma and retinal cell models in response to zinc stress; however, zinc binding negatively affects axogenic, differentiative and prosurvival functions of PEDF by suppressing its ability to activate receptor PEDF-R/PNPLA2. We suggest that glaucomatous neurodegeneration is associated with direct inhibition of PEDF signaling by extracellular zinc, making their complex a promising target for neuroprotective therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Toth, K. Zinc in neurotransmission. Annu Rev. Nutr.31, 139–153 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Sensi, S. L., Paoletti, P., Bush, A. I. & Sekler, I. Zinc in the physiology and pathology of the CNS. Nat. Rev. Neurosci.10, 780–791 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Kochanczyk, T., Drozd, A. & Krezel, A. Relationship between the architecture of zinc coordination and zinc binding affinity in proteins-insights into zinc regulation. Metallomics7, 244–257 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Ugarte, M. & Osborne, N. N. Recent advances in the understanding of the role of zinc in ocular tissues. Metallomics6, 189–200 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

