Anti-inflammatory and renoprotective effects of difelikefalin, a kappa opioid receptor agonist, in a rat model of renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 40596915
- PMCID: PMC12211451
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-025-04199-9
Anti-inflammatory and renoprotective effects of difelikefalin, a kappa opioid receptor agonist, in a rat model of renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: This study evaluated the effects of difelikefalin, a kappa opioid receptor (KOR) agonist, on the inflammatory response and renal dysfunction in a rat model of acute kidney injury induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, comparing it with other KOR agonists.
Methods: One week after right nephrectomy, rats received one of three drugs (difelikefalin, nalfurafine hydrochloride, or U-50488H). Thirty minutes later, ischemia was induced in the left kidney by clamping its artery and vein for 45 min. Rats were then transferred to metabolic cages for 24-h urine collection, and blood was taken at the 24-h time point. Renal function (blood urea nitrogen [BUN], serum creatinine [SCr], and creatinine clearance [CCr]) and 23 serum cytokines were assessed, along with histopathological evaluation of renal tubular damage.
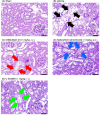
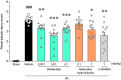
Results: Compared with the sham group, the vehicle group showed increased BUN and SCr levels, reduced CCr, and renal tubular damage. Difelikefalin improved BUN, SCr, and CCr levels and mitigated renal tubular damage. Similar effects were observed with nalfurafine hydrochloride and U-50488H. Thirteen serum cytokines were elevated in the vehicle group. Difelikefalin suppressed all elevated cytokines, U-50488H showed moderate efficacy, and nalfurafine hydrochloride exhibited little inhibitory effect.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that difelikefalin has anti-inflammatory and renoprotective effects in a rat acute kidney injury model, with varying anti-inflammatory efficacy among KOR agonists.
Keywords: Cytokine; Difelikefalin; Kappa opioid receptor; Nalfurafine hydrochloride; Renal ischemia–reperfusion injury.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was performed in accordance with our institutional guidelines, which conform to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Eighth Edition) and current Japanese regulations. The study was approved by the Laboratory Animal Care and Use Committee of the Central Research Laboratories of Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Committee approval numbers: 22A-006, 22B-043). The general condition of the animals was carefully monitored at least once a day to assess pain and distress. If serious signs of pain and distress had been observed—such as reduced reflexes, ataxic gait, or low body temperature—the affected animal would have been euthanized. All experimental procedures were performed with care to minimize pain and distress in the animals. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hesperetin attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by regulating ferroptosis in mice.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2523573. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2523573. Epub 2025 Jun 29. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40583332 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Renal Defensive Influence of Walnut Septa Extract Against Acute Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 Jun 12;2025:9713697. doi: 10.1155/mi/9713697. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40538499 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Melatonin in a Rat Model of Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury.Int J Urol. 2025 Jul;32(7):879-887. doi: 10.1111/iju.70054. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Int J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40213879
-
Ischaemic preconditioning for the reduction of renal ischaemia reperfusion injury.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 4;3(3):CD010777. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010777.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28258686 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Karimi Z, SoukhakLari R, Rahimi-Jaberi K, Esmaili Z, Moosavi M. Nanomicellar curcuminoids attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat through prevention of apoptosis and downregulation of MAPKs pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(2):1735–43. - PubMed
-
- Gholampour F, Roozbeh J, Janfeshan S, Karimi Z. Remote ischemic per-conditioning protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via suppressing gene expression of TLR4 and TNF-alpha in rat model. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;97(2):112–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

