Evaluating ocular torsion following inferior oblique weakening in superior oblique palsy: a pilot study using color fundus photography and spectral domain optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 40596931
- PMCID: PMC12220215
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-025-04205-6
Evaluating ocular torsion following inferior oblique weakening in superior oblique palsy: a pilot study using color fundus photography and spectral domain optical coherence tomography
Abstract
Purpose: To compare spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) and color fundus photography (CFP) for assessing ocular cyclotorsion in unilateral congenital superior oblique palsy (SOP) before and after inferior oblique disinsertion.
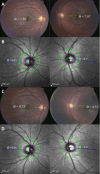
Methods: This prospective pilot study evaluated 18 patients (36 eyes) with unilateral congenital SOP. Disc-foveal angle (DFA) was measured preoperatively and 3 months postoperatively using CFP (analyzed with ImageJ) and Spectralis OCT (with FoDi software). Contralateral nonparetic eyes served as controls.
Results: Preoperative hypertropia (14.31 ± 4.15 prism diopter, PD) significantly improved postoperatively (1.46 ± 1.98 PD, P < 0.001). CFP measurements showed significantly greater cyclotorsion in paretic versus nonparetic eyes preoperatively (P = 0.001), while OCT revealed no inter-eye difference (P = 0.295). In paretic eyes, CFP-derived DFAs were significantly higher than OCT values both preoperatively (12.26 ± 4.72° vs. 8.87 ± 4.56°, P = 0.002) and postoperatively (7.25 ± 5.18° vs. 4.33 ± 3.98°, P = 0.005). Nonparetic eyes showed no significant inter-method differences at either timepoint (all P > 0.05). Inter-method reliability was moderate preoperatively (ICC = 0.693 paretic, 0.657 nonparetic) and improved postoperatively (ICC = 0.718 and 0.921, respectively). Bland-Altman analysis demonstrated narrowing limits of agreement postoperatively (nonparetic: 8.48° to 4.40°; paretic: 7.97° to 7.50°), with no systematic bias.
Conclusion: Spectralis OCT with FoDi software provides a clinically useful alternative to CFP for cyclotorsion assessment in congenital SOP, though it may systematically underestimate DFA values in paretic eyes.
Keywords: Congenital superior oblique palsy; Disc-foveal angle; FoDi software; Fundus photography; Inferior oblique weakening; Ocular torsion; Spectralis OCT; Vertical strabismus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Iran University of Medical Sciences (ethics code: IR.IUMS.REC.1401.421). The research adhered to the ethical guidelines stipulated in the Declaration of Helsinki. Prior to enrollment in the study, written informed consent was secured from all participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Flodin S, Pansell T, Rydberg A, Andersson Grönlund M. Clinical measurements of normative subjective cyclotorsion and cyclofusion in a healthy adult population. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020;98(2):177–81. 10.1111/aos.14201 - PubMed
-
- Georgievski Z, Sleep M, Koklanis K. Simulated torsional disparity disrupts horizontal fusion and stereopsis. J Am Assoc Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2007;11(2):120–4. 10.1016/j.jaapos.2006.09.022 - PubMed
-
- Raps EC, Solomon D, Galetta SL, Liu GT, Volpe NJ. Cyclodeviation in skew deviation. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994;118(4):509–14. 10.1016/S0002-9394(14)75804-0 - PubMed
-
- Fong JW, Hahn-Parrott LA, Siatkowski RM. Evaluation and management of symptomatic vertical strabismus and diplopia. J Binocul Vis Ocul Motil. 2022;72(4):226–9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36279479 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

