A retrospective propensity-matched study comparing whole-brain radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost to whole-brain radiotherapy alone for brain metastases
- PMID: 40596961
- PMCID: PMC12211532
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-025-14443-y
A retrospective propensity-matched study comparing whole-brain radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost to whole-brain radiotherapy alone for brain metastases
Abstract
Background: The effectiveness of whole brain radiation therapy with simultaneous integrated boost (WBRT-SIB) in comparison to whole brain radiation therapy alone (WBRT-alone) is yet unknown, despite the fact that its use in clinic is growing. To investigate the variations in intracranial control and overall survival (OS) between the two approaches, we conducted a matching comparison for patients with brain metastases (BM).
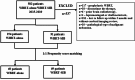
Method: From January 1, 2015, to December 31, 2019, a total of 245 BM patients were eligible for inclusion, including 154 patients who received WBRT-alone (30 Gy/10 fractions) and 91 patients who received WBRT-SIB (40-50 Gy/10 fractions). 1:1 propensity score matching was used to select the patients with balanced baseline characteristics. The intracranial control and OS condition were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method, Log-rank test, and Cox proportional hazard regression model.
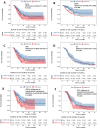
Results: 138 patients were matched into the WBRT-SIB group and the WBRT-alone group. Of these, 113 (81.9%) patients had BM originating from the lungs, and 124 (89.9%) patients had more than 3 intracranial lesions. After the initiation of radiotherapy, the WBRT-SIB group and the WBRT-alone group had respective 2-year intracranial progression-free survival (iPFS), local progression-free survival (iLPFS), and distant progression-free survival (iDPFS) of 46.2% and 24.5% (p = 0.017), 49.4% and 29.8% (p = 0.033), and 68.6% and 54.4% (p = 0.040). There was no significant difference in OS (22.2 vs. 19.0 months, p = 0.768). However, in the exploratory subgroup analysis of infratentorial with/without supratentorial metastases (n = 96), the WBRT-SIB group showed a significantly better OS than the WBRT-alone group (24.6 vs.17.2 months, p = 0.040). Furthermore, the Cox proportional hazard model of this subgroup revealed that WBRT-SIB (p = 0.039) and systemic therapy after radiotherapy (p = 0.002) were independent prognostic factors for OS. There was no difference in the incidence of grade 3-4 acute brain radiation reactions between the two groups (24.6% vs. 17.4%, p = 0.290).
Conclusion: WBRT-SIB is a promising strategy for patients with BM. Compared to WBRT alone, WBRT-SIB can significantly prolong the intracranial PFS (including local and distant PFS). Additionally, while WBRT-SIB did not improve OS in the entire cohort, the OS benefit for patients with BM accompanied by infratentorial involvement warrants further exploration.
Keywords: Brain metastases; Prognosis; Simultaneous integrated boost; Whole brain radiation therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: In accordance with ICH-GCP principles and relevant Chinese regulations/guidelines, the research proposal has been reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center for the conduct of this research. The Declaration of Helsinki, Ethical Review of Biomedical Research involving Human Subjects and other relevant international guidelines were strictly followed during the study. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Apr 18;2012(4):CD003869. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003869.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 25;1:CD003869. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003869.pub4. PMID: 22513917 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Comparison the efficiency of whole brain radiotherapy and simultaneous integrated boost in small cell lung cancer with brain metastases.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 24;25(1):1210. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14593-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40707906 Free PMC article.
-
Brain metastases of lung cancer: comparison of survival outcomes among whole brain radiotherapy, whole brain radiotherapy with consecutive boost, and simultaneous integrated boost.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Feb;147(2):569-577. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03359-8. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32851477 Free PMC article.
-
Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of multiple brain metastases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Jul 19;(3):CD003869. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003869.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Apr 18;(4):CD003869. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003869.pub3. PMID: 16856022 Updated.
-
Whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) alone versus WBRT and radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 25;9(9):CD006121. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006121.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28945270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A, Cancer statistics. 2014. CA A Cancer J Clinicians. 2014 [cited 2024 Apr 5];64:9–29. Available from: https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.3322/caac.21208
-
- Larson D, Sahgal A. Adjuvant whole brain radiotherapy: strong emotions decide but rationale studies are needed: in regard to, Brown et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2008;70:1305–1309). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;72:959. - PubMed
-
- Verger E, Gil M, Yaya R, Viñolas N, Villà S, Pujol T, et al. Temozolomide and concomitant whole brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: a phase II randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61:185–91. - PubMed
-
- Sperduto PW, Wang M, Robins HI, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Komaki R, et al. A phase 3 trial of whole brain radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery alone versus WBRT and SRS with Temozolomide or erlotinib for non-small cell lung cancer and 1 to 3 brain metastases: radiation therapy oncology group 0320. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85:1312–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roos DE, Smith JG, Stephens SW. Radiosurgery versus surgery, both with adjuvant whole brain radiotherapy, for solitary brain metastases: a randomised controlled trial. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2011;23:646–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

