A predictive model for WHO/ISUP pathologic grading of renal clear cell carcinoma based on CT radiomics: a multicenter study
- PMID: 40597030
- PMCID: PMC12211403
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-025-04268-z
A predictive model for WHO/ISUP pathologic grading of renal clear cell carcinoma based on CT radiomics: a multicenter study
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the predictive value of CT radiomics combined with clinical-imaging features for the WHO/ISUP pathological grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma(ccRCC).
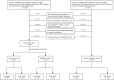
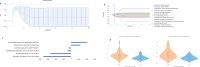
Methods: In this multicenter retrospective study enrolled 169 patients (110 males, 59 females) with pathological confirmed ccRCC between November 2017 and February 2022. Based on the WHO/ISUP pathological grading criteria, patients were stratified into two groups: low-grade (grades I-II, n = 93) and high-grade (grades III-IV, n = 76). Three-dimensional tumor segmentation was performed on CT cortical-phase images using ITK-SNAP software. The segmented data were subsequently processed through the United Imaging Intelligent Scientific Research Platform for radiomic feature extraction and selection. Logistic regression analyses were conducted to identify independent predictive factors. Based on these factors, an optimized predictive model was developed through random forest classification and evaluated using calibration curves, ROC analysis, Delong test and decision curve analysis.
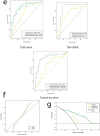
Results: Significant differences were observed in tumor size, morphology, hemorrhage, necrosis, tumor thrombus, capsular invasion and tumor extending beyond the renal margin between the two groups. Logistic regression analysis identified tumor size, hemorrhage and tumor thrombus as independent predictors. Six radiomic features were selected to establish prediction model. In the training cohort, the combined model demonstrated superior discriminative performance, achieving an AUC of 0.895, compared to the radiomics model (AUC = 0.873) and the clinical-imaging model (AUC = 0.712). The combined model also exhibited strong predictive ability in both the validation cohort (AUC = 0.885) and the external cohort (AUC = 0.860). DeLong tests revealed statistically significant differences in AUC between the combined model and the clinical-imaging model (Z = 3.023, P = 0.002), as well as between the radiomics model and the clinical-imaging model (Z = 2.560, P = 0.010). However, no significant difference in AUC was found between the combined model and the radiomics model (Z = 1.627, P = 0.103). Decision curve analysis revealed the combined model yielded enhanced net benefit across threshold ranges (0.1-0.84).
Conclusion: The combined model based on CT radiomics combined with clinical- imaging features can effectively predict the WHO/ISUP pathological grade of ccRCC, providing more basis for the prognosis assessment of patients.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Predictive model; Radiomics; Renal clear cell carcinoma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Human ethics and consent to participate: Approval for the study was granted by the Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, and due to the retrospective nature of the study, informed consent from patients was waived by Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Cancer Hospital. The study adhered to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Predictive value of CT-based tumor and peritumoral radiomics for WHO/ISUP grading of non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jul 15;105(26):2195-2202. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20250226-00460. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40660974 Chinese.
-
Computed tomography-based delta-radiomics analysis for preoperative prediction of ISUP pathological nuclear grading in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Sep;50(9):4289-4300. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-04857-4. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40024922
-
Development and validation of a nomogram combined pre-operative quantitative MR parameters for the prediction of pathological WHO/ISUP grade in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.World J Urol. 2025 Aug 9;43(1):480. doi: 10.1007/s00345-025-05864-2. World J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40782267
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dwivedi DK, Xi Y, Kapur P, Madhuranthakam AJ, Lewis MA, Udayakumar D, Rasmussen R, Yuan Q, Bagrodia A, Margulis V, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging radiomics analyses for prediction of High-Grade histology and necrosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: preliminary experience. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2020;19:12–e211. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mühlbauer J, Kowalewski KF, Walach MT, Porubsky S, Wessels F, Nuhn P, Wagener N, Kriegmair MC. Partial nephrectomy preserves renal function without increasing the risk of complications compared with radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinomas of stages pT2-3a. Int J Urol. 2020;27:906–13. - PubMed
-
- Zou XP, Ning K, Zhang ZL, Zou L, Xiong LB, Peng YL, Zhou ZH, Liu HM, Yu CP, Dong P, et al. Long-term survival analysis of 1 367 patients treated with radical nephrectomy from a single center. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023;45:981–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

