Paxlovid for the treatment of severe or critical COVID-19 in children
- PMID: 40597122
- PMCID: PMC12220247
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-025-05807-1
Paxlovid for the treatment of severe or critical COVID-19 in children
Abstract
Background: Paxlovid, known for its efficacy against SARS-CoV-2, is currently limited in its use for treating pediatric COVID-19, particularly in severe or critical cases.
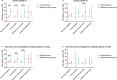
Methods: We conducted a study within a single-center, prospective cohort of 450 children diagnosed with COVID-19 between December 2022 and May 2023. This study included 30 pediatric patients who received Paxlovid and 60 matched controls who did not, based on factors such as age, disease severity, and underlying health conditions. Safety was assessed through the incidence of adverse events, and laboratory parameters. The time to clinical symptom improvement was the main efficacy outcome. Moreover, we calculated the AUC0 - 12 h of Nirmatrelvir of the Paxlovid patients.
Results: Adverse events occurred in 16.7% of both groups, with no serious events reported. The Paxlovid group showed a significantly shorter time to viral clearance, fever resolution, and symptom recovery compared to controls (4.9 vs. 11.0 days, P = 0.01; 11.2 vs. 16.4 days, P = 0.01; 4.6 vs. 17.6 days, P < 0.01). This effect was most noticeable in children with underlying conditions or those treated early. No significant differences were observed in ICU transfers or mortality (P > 0.05). The AUC₀-₁₂h of Nirmatrelvir did not significantly alter treatment outcomes.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that Paxlovid may be a safe and effective option for treating severe or critical COVID-19 in children.
Keywords: COVID-19; Children; Critical; Paxlovid; Pharmacokinetics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Children’s Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine (IRB No. 2023-IRB-0176-P-01). Informed consent was obtained from the legal guardians of all children in two groups. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2023 [Available from: https://covid19.who.int/October2023
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

