A bacteriophage-based virus-like particle vaccine induces cross-reactive neutralising antibodies against porcine epidemic diarrhoea viruses (PEDV)
- PMID: 40597367
- PMCID: PMC12210915
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-025-01559-z
A bacteriophage-based virus-like particle vaccine induces cross-reactive neutralising antibodies against porcine epidemic diarrhoea viruses (PEDV)
Abstract
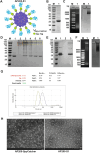
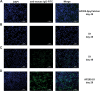
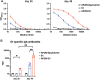
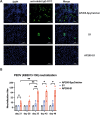
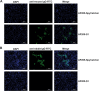
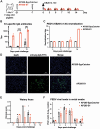
Although vaccines against porcine epidemic diarrhoea viruses (PEDV) are available, PED outbreaks continue to occur in many countries due to the emergence of new variants. Therefore, further endeavours are necessary to develop efficient and broadly protective vaccines. In this context, we present a nanoparticle vaccine candidate, referred to as AP205-S1, which successfully elicited antibody responses in mice and pigs. The vaccine was created by coupling the S1 protein of PEDV-KB2013, a G-II strain, to a bacterially expressed AP205-VLP using the SpyCatcher/SpyTag system. The AP205-S1 vaccine demonstrated an intact and homogenous viral particle structure, incorporating E. coli-derived ssRNA. Upon administration in mice, AP205-S1 induced high levels of S1-specific IgG antibodies in both serum and the gastrointestinal tract, particularly following a booster dose. Importantly, these antibodies were capable of neutralising PEDV in vitro, suggesting that the vaccine can generate protective antibodies against PEDV infection. Notably, the antibodies elicited by AP205-S1 exhibited cross-neutralising potential against a G-I strain, PEDV-AH2018-HF1, which was preserved in our lab. Additionally, S1-specific IgG antibodies were stimulated in piglets following immunisation with AP205-S1, and these antibodies could neutralise PEDV in vitro. Interestingly, piglets immunised with AP205-S1 exhibited lower viral loads compared to control piglets following a viral challenge. In conclusion, we developed a VLP-based vaccine candidate against PEDV, which demonstrated excellent immunogenicity in both mice and piglets, potentially providing protection against viral infection. Our work offers an effective option for preventing future PEDV epidemics.
Keywords: AP205-VLP; PEDV; neutralizing antibody; vaccine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments followed the Animal Ethics Procedures and Guidelines of the People’s Republic of China. The mouse experiment protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Anhui Agricultural University (Approval No. SYXK (Anhui) 2016-007). The pig experiment protocols were approved by the Animal Welfare Committee of Northwest A&F University (Approval No. ICAUC-2024-CVM032). Competing interests: Lisha Zha is involved in a pet vaccine company and owns shares. All the other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A recombinant adenovirus-vectored PEDV vaccine co-expressing S1 and N proteins enhances mucosal immunity and confers protection in piglets.Vet Microbiol. 2025 Sep;308:110633. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2025.110633. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Vet Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40651152
-
Engineering a recombination-resistant live attenuated vaccine candidate with suppressed interferon antagonists for PEDV.J Virol. 2025 Jul 22;99(7):e0045125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00451-25. Epub 2025 Jun 12. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40503881 Free PMC article.
-
Ferritin-based nanoparticle vaccine protects neonatal piglets against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus challenge following immunization of pregnant sows.Vet Res. 2025 Jul 7;56(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01542-8. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40624655 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine as a promising choice for future control of PEDV.Virus Res. 2025 Jun;356:199572. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2025.199572. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Virus Res. 2025. PMID: 40220931 Review.
References
-
- Li M, Pan YY, Xi Y, Wang M, Zeng QY (2023) Insights and progress on epidemic characteristics, genotyping, and preventive measures of PEDV in China: a review. Microb Pathog 181:106185 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

