Microbiome-based therapeutics towards healthier aging and longevity
- PMID: 40597414
- PMCID: PMC12220006
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-025-01493-x
Microbiome-based therapeutics towards healthier aging and longevity
Abstract
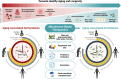
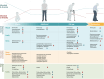
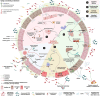
The gut microbiome is our lifetime companion, regulating our health from birth throughout the lifespan. The gut microbiome composition changes continually with age, influencing both physiological and immunological development. Emerging evidence highlights the close association, and thus implication, of the microbiome with healthy disease-free aging and longevity. Accordingly, targeting the gut microbiome is emerging as a promising avenue to prevent, alleviate, and ameliorate aging-related disorders. Herein, we provide a prospective and inclusive framework of the close connection of the gut microbiome with human aging, while contemplating how this association is intertwined with age-related diseases. We delve into recently emerging and potential microbiome-based therapeutics that are projected to aid in alleviating myriad aging-related diseases, thereby enhancing the health and well-being of the aging population. Finally, we present a foundation and perspective underlining the prospects of microbiome-based therapeutics developed and tailored precisely for the elderly, with the overarching goal of promoting health and longevity.
Keywords: Dysbiosis; Geriatrics; Gut; Inflammaging; Metagenomics; Microbiota; Postbiotics; Prebiotics; Probiotics; Senescence.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Conway J, Duggal NA. Ageing of the gut microbiome: Potential influences on immune senescence and inflammageing. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;68: 101323. - PubMed
-
- Pang S, Chen X, Lu Z, Meng L, Huang Y, Yu X, et al. Longevity of centenarians is reflected by the gut microbiome with youth-associated signatures. Nat Aging. 2023;3:436–49. - PubMed
-
- Martino C, Dilmore AH, Burcham ZM, Metcalf JL, Jeste D, Knight R. Microbiota succession throughout life from the cradle to the grave. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

