A nomogram based on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging radiomics for prediction of acute pancreatitis activity
- PMID: 40597753
- PMCID: PMC12220396
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-025-01778-y
A nomogram based on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging radiomics for prediction of acute pancreatitis activity
Abstract
Purpose: In acute pancreatitis (AP), disease activity is defined as the reversible manifestation of the disease. The aim of this study was to develop a nomogram for predicting disease activity in AP based on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) radiomics.
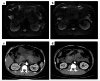
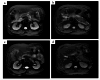
Methods: This retrospective study included 310 patients with first-episode AP from two medical centers in China. Patients from the first medical center were randomly divided into a training cohort (n = 122) and an internal validation cohort (n = 123) in a 5:5 ratio. Patients from the second medical center were used as the external independent validation cohort (n = 65). Radiomics features were extracted from multiparametric MRI images based on pancreatic parenchymal regions. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) was used for feature screening, logistic regression was used to establish radiomic feature, and statistically significant laboratory parameters were incorporated to construct the nomogram. The area under the receiver operator characteristic curve assessed the predictive performance of the nomogram. Furthermore, decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to assess the clinical utility of the nomogram, and the disease activity was validated against follow-up clinical outcomes (e.g., organ failure progression, ICU admission) and imaging-confirmed changes within one-week after MRI.
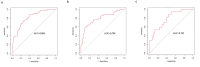
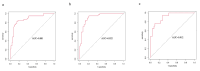
Results: The AUCs of the radiomic signature were 0.808 (training cohort), 0.789 (internal validation cohort), and 0.783 (external validation cohort). Radiomic signature, extrapancreatic inflammation on MRI (EPIM) scores, and WBC count were identified as independent risk factors for the activity of AP and were therefore included in the nomogram. The AUC of the nomogram were 0.881 (training cohort), 0.922 (internal validation cohort) and 0.912 (external validation cohort). Additionally, the nomogram model obtained the greatest net benefit, according to the results of decision curves Based on the follow-up results, we also found that AP patients with higher disease activity were more likely to experience exacerbations.
Conclusions: This nomogram can accurately predict the activity of AP patients, thus providing objective monitoring of the patient's course and potentially improving patient prognosis.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Disease activity; Magnetic resonance imaging; Radiomic nomogram.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: This study was conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional review board of Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (file number 2023ER314-1). Acquisition of informed consent from patients was waived owing to the retrospective nature of this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Individual consent for this retrospective analysis was waived by the Ethics Committee. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiomics Nomogram Based on Optimal Volume of Interest Derived from High-Resolution CT for Preoperative Prediction of IASLC Grading in Clinical IA Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Multi-Center, Large-Population Study.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241300734. doi: 10.1177/15330338241300734. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39569528 Free PMC article.
-
A novel MRI-based radiomics for preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion in rectal cancer.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Aug;50(8):3377-3390. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-04800-7. Epub 2025 Jan 12. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39799548
-
Development of a Radiomic-clinical Nomogram for Prediction of Survival in Patients with Nasal Extranodal Natural Killer/T-cell Lymphoma.Curr Med Imaging. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.2174/0115734056319914250605053257. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40551696
-
Multiparametric radiomic analysis of MRI for predicting satellite nodules and recurrence-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Oct;122:110450. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2025.110450. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40532770 Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Paragomi P, Hinton A, Pothoulakis I, Talukdar R, Kochhar R, Goenka MK, Gulla A, Gonzalez JA, Singh VK, Bogado MF, et al. The modified pancreatitis activity scoring system shows distinct trajectories in acute pancreatitis: an international study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(6):1334–e13421334. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG, Vege SS. Classification of acute pancreatitis–2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62(1):102–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

