The effect of carvacrol on kidney injury caused by isopreterenol-induced myocardial infarction
- PMID: 40597757
- PMCID: PMC12211812
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-025-04245-6
The effect of carvacrol on kidney injury caused by isopreterenol-induced myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Myocardial infarction is a major cause of morbidity and mortality, often leading to heart and kidney dysfunction. Despite advancements in treatment, the link between heart and kidney damage is poorly understood. This study aims to evaluate the potential protective effect of Carvacrol, a natural bioactive compound, on kidney injury induced by myocardial infarction.
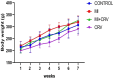
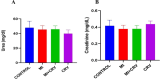
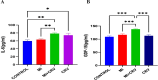
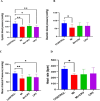
Methods: In this experimental study, 32 male Wistar rats were divided into four groups: Control, Carvacrol (50 mg/kg), Myocardial Infarction (85 mg/kg isoproterenol), and Myocardial Infarction + Carvacrol (50 mg/kg Carvacrol + 85 mg/kg isoproterenol). Carvacrol was administered for six weeks, and myocardial infarction was induced with isoproterenol. Blood pressure, biochemical parametres (creatinin kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, urea, creatinine, GDF-15, IL-6), and kidney tissue histopathology were evaluated.
Results: Biochemical analysis showed increased Creatinin Kinase and Lactate Dehydrogenase levels in the Myocardial Infarction group compared to controls(p = 0.023, p = 0.020), with carvacrol reducing these markers. IL-6 and GDF-15 levels were elevated in both the Myocardial Infarction and Myocardial Infarction + Carvacrol groups (p = 0.009, p < 0.001). Blood pressure was significantly reduced in the Myocardial Infarction group. Histopathological examination revealed severe kidney damage in the Myocardial Infarction group, while Carvacrol treatment showed less kidney damage, with only mild tubular dilation and rare necrosis.
Conclusion: Carvacrol appears to have protective effects against kidney injury in myocardial infarction. It reduced myocardial injury markers and kidney damage, suggesting its potential therapeutic use in cardiorenal syndrome. Further studies are needed to understand its mechanisms and clinical applications in cardiovascular and renal diseases.
Keywords: Carvacrol; Isopreterenol; Kidneys; Myocardial infarction; Rat.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The experiments were conducted in accordance with the revised Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 in the UK and Directive 2010/63/EU in Europe. Ethical approval was obtained from Kirsehir Ahi Evran University Local Ethics Committee for Animal Experiments (Aprroval number: 2024-08-7). Consest for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cardioprotective effects of carvacrol in the isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction model.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jul 14;26(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00967-3. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40660388 Free PMC article.
-
JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor baricitinib ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Sep 5;1002:177770. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177770. Epub 2025 May 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40441588
-
Effects of nerolidol on serum cytokines in acute myocardial infarction: insights into the asprosin, spexin, and DARS2 antibodies in the brain cortex.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 18;52(1):734. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10842-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40679581
-
Levetiracetam add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy: an updated Cochrane Review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD001901. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001901.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972056 Free PMC article.
-
Foetal haemoglobin inducers for reducing blood transfusion in non-transfusion-dependent beta-thalassaemias.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 13;1(1):CD013767. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013767.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36637054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costanzo MR. The cardiorenal syndrome in heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. 2020;16(1):81–97. - PubMed
-
- Ronco C, Di Lullo L. Cardiorenal syndrome. Heart Fail Clin. 2014;10(2):251–80. - PubMed
-
- Abdelzaher WY, Ahmed SM, Welson NN, Alsharif KF, Batiha GE-S, Labib DAA. Dapsone ameliorates isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction via Nrf2/HO-1; TLR4/TNF-α signaling pathways and the suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:669679. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

