Evaluating ChatGPT and DeepSeek in postdural puncture headache management: a comparative study with international consensus guidelines
- PMID: 40597769
- PMCID: PMC12211737
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-025-04280-8
Evaluating ChatGPT and DeepSeek in postdural puncture headache management: a comparative study with international consensus guidelines
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the use of ChatGPT and DeepSeek in clinical practice to provide healthcare professionals with accurate information on the prevention, diagnosis, and management of post-dural puncture headache (PDPH), in particular to evaluate ChatGPT-4o, ChatGPT-4o mini, DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek with Deep Think(R1)'s responses with consensus practice guidelines for headache after dural puncture.
Background: Post-dural puncture headache (PDPH) is a common complication of dural puncture. Currently, there is a lack of evidence-based guidance on the prevention, diagnosis and management of PDPH. The 2023 Consensus guidelines provide comprehensive information. With the development and popularization of AI, more and more people are using ai models, including patients and doctors. However, the quality of the answers provided by ai has not yet been tested.
Methods: Responses from ChatGPT-4o, ChatGPT-4o mini, DeepSeek-V3, and DeepSeek-R1 were evaluated against PDPH guidelines using four dimensions: Accuracy (guideline adherence), Overconclusiveness (unjustified recommendations), Supplementary information (additional relevant details), and Incompleteness (omission of critical guidelines). A 5-point Likert scale further assessed response accuracy and completeness.
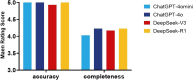
Results: All four models show high accuracy and completeness.Of the 10 clinical guidelines evaluated,ChatGPT-4o, ChatGPT-4o mini, DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1 all showed 100% accuracy in responses (10/10)(p = 1). None of the four models showed overly conclusive results(p = 1). In terms of supplementary information, ChatGPT-4o,ChatGPT-4o mini and DeepSeek-R1 are 100% (10/10), DeepSeek-V3 is 90% (9/10)(p = 1). In terms of incompleteness, ChatGPT-4o is 80%(8/10), DeepSeek-R1 is 70%(7/10), ChatGPT-4o mini and DeepSeek-V3 are 60% (6/10) (p = 0.729).
Conclusion: All four AI models demonstrate clinical validity, with ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-R1 showing stronger guideline alignment. Though largely accurate, their responses achieve only 60-80% completeness relative to medical guidelines. Healthcare professionals must exercise caution when using AI tools and should critically evaluate outputs before clinical application. While promising, their partial guideline coverage requires careful human oversight. Further validation research is essential before these models can reliably support clinical decision-making for complex conditions like PDPH.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; ChatGPT; DeepSeek; Postdural puncture headache.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Goh E, Gallo R, Hom J, Strong E, Weng Y, Kerman H, Cool JA, Kanjee Z, Parsons AS, Ahuja N, Horvitz E, Yang D, Milstein A, Olson A, Rodman A, Chen JH. Large Language Model Influence on Diagnostic Reasoning: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(10): e2440969. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.40969. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuczkowski KM. Post-dural puncture headache in the obstetric patient: an old problem New solutions. Minerva Anestesiol. 2004;70(12):823–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources