Overexpression of KRAS enhanced the stemness of esophageal cancer cells inhibited by overexpression of circ0043898
- PMID: 40597918
- PMCID: PMC12210846
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-025-14358-8
Overexpression of KRAS enhanced the stemness of esophageal cancer cells inhibited by overexpression of circ0043898
Abstract
Background: Our previous study revealed that circ0043898 is downregulated in esophageal cancer (EC), and its overexpression attenuates the progression of EC. The objective of this article is to explore whether circ0043898 inhibits tumor progression by inhibiting cancer stem cells (CSCs) in EC.
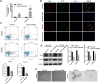
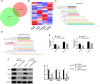
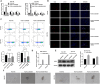
Methods: PCDH-circ0043898 plasmid was transfected into EC cells, and the effect of overexpression was verified by qRT-PCR. Immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and stem cell spheroidization were used to detect CSCs phenotype changes. RNA sequencing was adopted to identify downstream regulatory genes and p-PI3K, PI3K, and KRAS expressions were validated by western blot. To investigate whether KRAS functions downstream of circ0043898 in regulating cancer stemness, we co-transfected EC cells with both KRAS and circ0043898 plasmids and examined CSCs phenotypes.
Results: circ0043898 was overexpressed in the EC cells, and reduced stem cell markers (CD44 and CD133) and the number of stem cell spheroidization. In addition, overexpression of circ0043898 changed many genes expression, including reduced p-PI3K, PI3K, and KRAS expressions. Moreover, overexpression of KRAS attenuated the effect of overexpressed circ0043898 on CSCs phenotype.
Conclusions: Overexpression of circ0043898 reduced CSCs markers and the number of stem cell spheroidization. However, the overexpression of KRAS attenuated the inhibition effect of overexpressed circ0043898 on CSCs marker and the number of stem cell spheroidization. These findings identify a potential therapeutic target for the EC.
Keywords: CircRNAs; Esophageal cancer; KRAS; Stemness; circ0043898.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epicatechin attenuates the stemness of liver cancer stem cells and tumorigenesis through DNA methylation-mediated inactivation of GINS1/HRAS.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 25;23(1):828. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06790-y. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40713555 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Head and Neck Squamous Cancer Stem Cells by PI3K and SOX2.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016 Sep 15;109(1):djw189. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw189. Print 2017 Jan. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016. PMID: 27634934 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via EGFR degradation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05259-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594106 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors for metastatic colorectal cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 27;6(6):CD007047. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007047.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28654140 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 14;9(9):CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11:CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub7. PMID: 34519354 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Zhu H, et al. Esophageal cancer in China: practice and research in the new era. Int J Cancer. 2023;152:1741–51. 10.1002/ijc.34301. - PubMed
-
- Waters JK, Reznik SI. Update on management of squamous cell esophageal Cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022;24:375–85. 10.1007/s11912-021-01153-4. - PubMed
-
- Lewis S, Lukovic J. Neoadjuvant therapy in esophageal Cancer. Torac Surg Clin. 2022;32:447–56. 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2022.06.003. - PubMed
-
- Fu Z, et al. CELF6 as an oncogene in colorectal cancer: targeting Stem-Cell-Like properties through modulation of HOXA5 mRNA stability. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024;29:395. 10.31083/j.fbl2911395. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

