Decreased miR-455-3p promotes diabetic retinopathy progression via modulating retinal endothelial proliferation and apoptosis
- PMID: 40597930
- PMCID: PMC12220737
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-025-04179-5
Decreased miR-455-3p promotes diabetic retinopathy progression via modulating retinal endothelial proliferation and apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is one of the common ocular complications of diabetes. Recent studies have also found that miR-455-3p is dysregulated in DR. However, its underlying mechanisms warrant further investigation.
Objective: This study focused on the clinical value of miR-455-3p and its regulatory mechanisms in DR.
Materials and methods: This study recruited 130 patients with DR and 105 healthy individuals. HRMECs treated with high glucose were used to simulate DR conditions. The expression of miR-455-3p and Integrin beta 1(ITGB1) were assessed by qRT-PCR while the target relationship between them was validated via Dual-luciferase reporter assay. ROC curve was utilized for the diagnostic performance. CCK-8 and flow cytometry were employed for proliferation and apoptosis measurement while ELISA was used for inflammation.
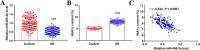
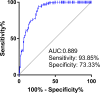
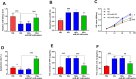
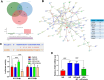
Results: Serum miR-455-3p was found to be distinctly downregulated in patients with DR. The expression of serum miR-455-3p was negatively associated with HbA1c levels in patients with DR. The miR-455-3p also exhibited strong diagnostic potential for distinguishing patients with DR from healthy individuals. In high glucose-induced HRMECs, miR-455-3p was significantly downregulated. miR-455-3p can target and negatively regulate ITGB1, thereby inhibiting the proliferation and inflammation of HRMECs induced by high glucose and promoting cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: Decreased miR-455-3p promotes diabetic retinopathy progression via negative regulation on ITGB1.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: ITGB1; Diabetic retinopathy; Proliferation; miR-455-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Taizhou First People’s Hospital before the study began. The written informed consent has been obtained from the participants involved. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Grochowski ET, Pietrowska K, Godlewski A, Gosk W, Buczynska A, Wojnar M et al. Simultaneous comparison of aqueous humor and serum metabolic profiles of diabetic and nondiabetic patients undergoing cataract Surgery-A targeted and quantitative metabolomics study. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24(16). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pelikanova T. [Diabetic retinopathy: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications]. Vnitr Lek. 2016;62(7–8):620–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

