Association between serum tumor markers and diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients: a cross-sectional survey in Western China
- PMID: 40598128
- PMCID: PMC12211909
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-025-01932-1
Association between serum tumor markers and diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients: a cross-sectional survey in Western China
Abstract
Background: Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a common and serious microvascular complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, there is limited clinical research on the use of tumor markers in DN, and the relationship between serum tumor markers and DN in T2DM patients is not well understood.
Purpose: This study seeks to examine the potential association between serum tumor biomarkers and DN in individuals with T2DM in Western China.
Methods: This cross-sectional study involved 620 T2DM patients, including 253 with DN and 367 without. Differences between the groups were analyzed using Student's t-test, Mann-Whitney U-test, and Pearson's Chi-squared test. Logistic regression assessed the link between serum tumor biomarkers and DN presence, while Spearman's correlation analyzed the relationship between these biomarkers and kidney damage indicators. The diagnostic efficacy of the biomarkers was evaluated through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
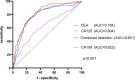
Results: In patients with T2DM and DN, the serum levels of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), neuron-specific enolase (NSE), cancer antigen 211 (CA211), cancer antigen 125 (CA125), cancer antigen 199 (CA199), and squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC) were significantly elevated compared to those in the non-DN group, while serum levels of pro-gastrin-releasing peptide (ProGRP) were lower than those in the DN group (P < 0.01). After adjusting for potential confounding variables, serum levels of CEA, CA199, and CA125 were found to be independently associated with DN in T2DM patients. The odds ratio (OR) for elevated CEA in relation to DN was 1.41 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.17-1.70), for elevated CA125 was 1.02 (95% CI: 1.005-1.036), and for elevated CA199 was 1.021 (95% CI: 1.010-1.032). In this study, the levels of CA125 and CA199 exhibited a negative correlation with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), with correlation coefficients of -0.16, and -0.089, respectively. Conversely, these biomarkers were positively correlated with albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR), with correlation coefficients of 0.56, 0.55, and 0.22, respectively, and with cystatin C levels, with correlation coefficients of 0.17, 0.23, and 0.07, respectively. ROC curve analysis showed that combining CEA, CA125, and CA199 improves the accuracy in distinguishing DN patients, with an AUC of 0.82 (95% CI: 0.79-0.86, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: This study shows that serum tumor markers (CEA, CA125, and CA199) are strongly linked to the presence of DN in type 2 diabetes patients, providing new insights into their role in DN and suggesting potential prevention strategies.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: Chinese population of Northwest China; Diabetic nephropathy; Diagnosis; Tumor markers; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval for the study was granted by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, which also provided a waiver of consent due to the exclusive use of retrospective data devoid of personal identifying information. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical value of free ubiquitin in the identification of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and preliminary exploration of its protective effect.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 17;26(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04219-8. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40676522 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and prediction of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by using an advanced biomarkers.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2025 Jun-Jul;45(6):101330. doi: 10.1016/j.nefroe.2025.101330. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2025. PMID: 40783305
-
Decreased Serum Adipose Triglyceride Lipase Level Is Associated With Renal Function Impairment in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2025 Jul 24;2025:9987648. doi: 10.1155/jdr/9987648. eCollection 2025. J Diabetes Res. 2025. PMID: 40747293 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.Health Technol Assess. 2005 Aug;9(30):iii-vi, xiii-163. doi: 10.3310/hta9300. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 16095545
-
Altered dietary salt intake for preventing diabetic kidney disease and its progression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 16;1(1):CD006763. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006763.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36645291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaur R, Dahiya L, Kumar M. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase inhibitors: A new valid approach for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;141:473–505. - PubMed
-
- Hu C, Jia W. Diabetes in China: epidemiology and genetic risk factors and their clinical utility in personalized medication. Diabetes. 2018;67,(1):3–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

