A sialic acid-binding protein in Toxoplasma gondii contains a conserved globular domain in apicomplexan parasites
- PMID: 40598570
- PMCID: PMC12210739
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-025-06845-5
A sialic acid-binding protein in Toxoplasma gondii contains a conserved globular domain in apicomplexan parasites
Abstract
Background: Apicomplexan protozoans employ an intricate invasion mechanism involving dynamic interactions with host cells, characterized by sequential secretion of adhesins and lectins. Our laboratory previously identified TgSABP1, a novel Toxoplasma gondii adhesin, demonstrating specific binding affinity for sialic acid (SA) receptors on host cell surfaces. However, the structural determinants governing SA recognition by this adhesin remain undefined.
Methods: Three-dimensional structural predictions of TgSABP1 and homologous proteins were generated using AlphaFold2. Bio-layer interferometry (BLI) quantified the binding affinities between the recombinant proteins and ligands. Competitive BLI assays evaluated small molecules that potentially inhibit the TgSABP1-sialyllactose interactions. Molecular docking simulations employing AutoDock Vina software elucidated ligand-binding site interactions. In vitro invasion inhibition assays were performed to assess the therapeutic potential of lead compounds targeting TgSABP1 against T. gondii tachyzoites.
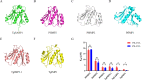
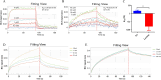
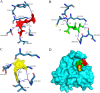
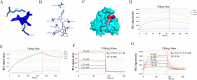
Results: AlphaFold2 structural predictions revealed that TgSABP1 and its homologues contain a conserved globular domain (pLDDT > 90) with significant structural homology (with root-mean-square deviation [RMSD] < 4 Å) to a Plasmodium falciparum invasion-related protein PfIMP2 (PDB: 5LG9). BLI quantification demonstrated the micromolar binding affinities of the recombinant proteins for 3'-sialyllactose-polyacrylamide (PAA) and 6'-sialyllactose (6'SL)-PAA. Intriguingly, although recombinant TgSABP1 showed stronger lactose binding (KD = 0.02 ± 0.01 M) compared to SA (KD = 2.07 ± 0.45 M), only the latter exhibited an inhibition on the TgSABP1-6'SL-PAA interaction. Virtual screening of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved compounds identified eltrombopag as a high-affinity molecule (ΔGbind = -8.3 kcal/mol) targeting the SA-binding pocket in TgSABP1. Functional validation demonstrated that eltrombopag effectively blocked the TgSABP1/6'SL-PAA interaction and significantly decreased host cell invasion of T. gondii tachyzoites.
Conclusions: Our study reveals a conserved globular domain of apicomplexan parasites as a novel SA-binding domain. Structural and functional characterization demonstrates its critical role in mediating TgSABP1-host cell interactions. Targeting this SA-binding pocket with eltrombopag effectively decreased T. gondii tachyzoite invasion, suggesting its therapeutic potential as an anti-invasion target. These findings not only elucidate a conserved mechanism underlying host receptor recognition in apicomplexans, but also establish a structural framework for the rational design of broad-spectrum inhibitors targeting invasion-related lectin domains.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; Globular domain; Sialic acid.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Friedrich N, Santos JM, Liu Y, Palma AS, Leon E, Saouros S, et al. Members of a novel protein family containing microneme adhesive repeat domains act as sialic acid-binding lectins during host cell invasion by apicomplexan parasites. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:2064–76. 10.1074/jbc.M109.060988. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

