EBNA leader protein orchestrates chromatin architecture remodeling during Epstein-Barr virus-induced B cell transformation
- PMID: 40598900
- PMCID: PMC12214021
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf629
EBNA leader protein orchestrates chromatin architecture remodeling during Epstein-Barr virus-induced B cell transformation
Abstract
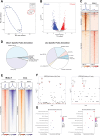
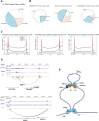
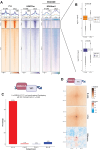
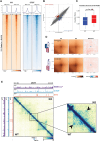
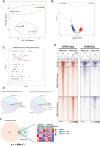
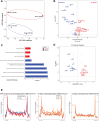
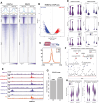
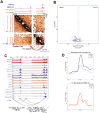
Epstein-Barr virus Nuclear Antigen Leader Protein (EBNA-LP) plays a pivotal role in the transformation of B cells by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), functioning independently of EBNA2 to regulate chromatin architecture and gene expression. Our study reveals that EBNA-LP binds to chromatin regions distinct from EBNA2 and facilitates the formation of long-distance chromatin loops by interacting with the cellular factor YY1. This interaction reconfigures the three-dimensional structure of the host genome, enhancing the integrity of topologically associating domains (TADs) and promoting the interaction between enhancers and promoters within these domains. In EBV-infected B cells, EBNA-LP strengthens YY1-mediated chromatin loops within TADs, which helps maintain stable regulatory programs essential for B cell transformation. Notably, EBNA-LP is crucial for establishing EBV-induced enhancers, yet it is not required for their maintenance once formed. Additionally, our data suggest a compensatory increase in CTCF binding in the absence of EBNA-LP, leading to more promiscuous chromatin interactions between TADs and a reduced TAD insulation at their boundaries. These findings provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms by which EBV reshapes the host genome chromatin architecture to support B cell transformation and highlight potential therapeutic targets for disrupting EBV-driven oncogenesis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

