Inflammatory biomarkers for predicting postoperative atrial fibrillation in cardiac surgery
- PMID: 40599146
- PMCID: PMC12207702
- DOI: 10.25122/jml-2025-0085
Inflammatory biomarkers for predicting postoperative atrial fibrillation in cardiac surgery
Abstract
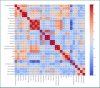
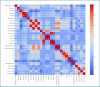
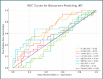
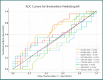
Postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) is a frequent complication of cardiac surgery associated with adverse outcomes. Systemic inflammation is implicated in POAF pathogenesis, suggesting inflammatory biomarkers may have predictive value. This study investigated the predictive capacity of readily accessible inflammatory markers for POAF during the early postoperative period in the cardiac intensive care unit, particularly within the 48-72-hour window when POAF most commonly occurs. In this prospective, single-center study, we enrolled 70 patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. We measured preoperative and postoperative (24h, 48h) levels of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-17A (IL-17A). POAF was systematically monitored. We assessed the predictive value of these markers using ROC curve analysis and logistic regression, adjusting for clinical risk factors. The coronary cohort showed that the NLR at both 24 hours and 48 hours were the most discriminative markers for predicting POAF, with PCR at 48 hours achieving a moderate AUC of 0.66. In multivariate regression models, PCR at 48 hours (P = 0.009) and age (P = 0.046) emerged as significant predictors, while NLR and CPB duration were moderately correlated with the occurrence of POAF. In contrast, within the valvular patient subgroup, the NLR again exhibited promising predictive value, along with increased markers of tissue injury such as CK, LDH, and creatinine. Readily accessible postoperative inflammatory markers, particularly NLR at 24 hours and CRP at 48 hours, demonstrated moderate predictive value for POAF in patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery. These markers, especially NLR and CRP, may potentially contribute to improved POAF risk stratification in clinical practice when combined with clinical risk factors. Furthermore, our analysis also indicates that preoperative IL-17A levels may influence the occurrence of POAF. Therefore, alongside CRP and NLR, preoperative IL-17A can be considered a potentially significant marker for atrial fibrillation following cardiac surgery. However, these findings are preliminary and require validation in larger, multi-center studies to confirm their clinical utility and inform preventative strategies.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; IL-17A; IL-6; atrial fibrillation; cardiac surgery; inflammation; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR); systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI).
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of postoperative atrial fibrillation on complications and mortality following Ivor Lewis esophagectomy for esophageal cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22305. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06239-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596337 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Sex-based differences in inflammatory predictors of outcomes in patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy: an inverse probability weighting analysis.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2025 Jun 21;18:17562864251345719. doi: 10.1177/17562864251345719. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2025. PMID: 40547862 Free PMC article.
-
Haematological indices as predictors of atrial fibrillation following isolated coronary artery bypass grafting, valvular surgery, or combined procedures: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Kardiol Pol. 2018;76(1):107-118. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2017.0179. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Kardiol Pol. 2018. PMID: 28980298
-
Predictive value of systemic inflammatory indices for perinatal outcomes following cervical cerclage: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jul 10;25(1):750. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07888-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40640782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hussain SMA, Harky A. Complications of coronary artery bypass grafting. Int J Med Rev. 2019;6:1–5. doi: 10.29252/IJMR-060101. - DOI
-
- Sadlonova M, Vogelgsang J, Lange C, Günther I, Wiesent A, Eberhard C, et al. Identification of risk factors for delirium, cognitive decline, and dementia after cardiac surgery (FINDERI-find delirium risk factors): a study protocol of a prospective observational study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Jun 30;22(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02732-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
