[Association Between Surrogate Markers of Insulin Resistance and Incident Cardiovascular Disease in a Population With Stages 0-3 Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: A Prospective Cohort Study]
- PMID: 40599269
- PMCID: PMC12207030
- DOI: 10.12182/20250360503
[Association Between Surrogate Markers of Insulin Resistance and Incident Cardiovascular Disease in a Population With Stages 0-3 Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: A Prospective Cohort Study]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association between 8 insulin resistance (IR) surrogate markers and incident atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) in population with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome (CKM) of stages 0-3, and to identify the surrogate marker with the best predictive performance.
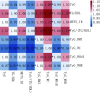
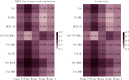
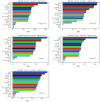
Methods: A study was conducted on 20121 community residents classified as CKM stages 0-3 from the Chengdu cohort of the China Multi-Ethic Cohort. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to calculate hazard ratios (HRs) between each IR surrogate marker and incident ASCVD. Cubic spline regression was employed to explore the dose-response relationships between these markers and incident ASCVD. The relative relationships between different markers and incident ASCVD were examined through the ratio of HRs (RHRs). Time-dependent area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (TDAUC) and Uno's C-statistic were calculated to compare the predictive performance of each marker for incident ASCVD. Based on the PREVENT equation components and the 8 surrogate markers under analysis, random forest feature selection was used to determine the contribution of each marker to accurate prediction.
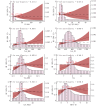
Results: During a follow-up period of 82741.93 person-years, 1447 incident cases of ASCVD were recorded, with an incidence density of 17.49 per 1000 person-years. Association analyses indicated that the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (TG/HDL) and the TyG/(TG/HDL) index were not associated with incident ASCVD (P > 0.05). The TyG index combined with obesity measurement parameters emerged as a reliable predictor of ASCVD incidence. The most promising indicator, TyG index with waist-to-height ratio (TyG_WHtR), exhibited an inverted J-shaped association with incident ASCVD (P for nonlinearity = 0.045; TDAUC = 0.640; C = 0.634), while the TyG index with body mass index (TyG_BMI), waist circumference (TyG_WC), and waist-to-hip ratio (TyG_WHR) showed positive linear associations (all P for trend < 0.05), with relatively lower predictive performance (C = 0.564, 0.588, and 0.598, respectively). Although both the TyG index and the metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) were associated with increased ASCVD risk (TyG: Q2 vs. Q1, HR = 1.23 and Q4 vs. Q1, HR = 1.24; METS-IR: P for non-linearity = 0.045), they exhibited poor predictive performance for incident ASCVD.
Conclusion: The TyG index combined with obesity measurement parameters is an ideal IR surrogate marker for predicting incident ASCVD in populations with stages 0-3 CKM. Monitoring these markers will facilitate the prevention and control of cardiovascular diseases in CKM populations.
目的: 探讨心肾代谢综合征(cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome, CKM)0-3期人群中8种胰岛素抵抗(insulin resistance, IR)替代标志物与新发动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病(atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, ASCVD)的关联,并选出预测性能最佳的替代指标。
方法: 基于西南区域自然人群队列成都地区人群,对其中处于CKM 0-3期的20121名社区居民开展研究。采用Cox比例风险模型计算各IR替代指标与新发ASCVD间的风险比(HR),采用立方样条回归探讨各指标与新发ASCVD间的剂量反应关系。通过风险比之比(RHR)探讨各指标与新发ASCVD间关联的相对关系。计算时间依赖的受试者工作特征曲线下面积(TDAUC)和Uno's C统计量,比较各指标对新发ASCVD的预测性能。最后基于PREVENT等式成分和8种待析指标进行随机森林特征选择,明确各指标对准确预测的贡献程度。
结果: 在82 741.93人年的随访期内共计发病1 447人,发病密度为每千人年17.49。关联分析显示,甘油三酯-高密度脂蛋白比值(TG/HDL)和甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数(TyG)/(TG/HDL)与新发ASCVD无关(P>0.05)。结合肥胖测量参数的TyG是预测ASCVD发病的可靠指标,其中最具潜能的结合腰高比的甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数(TyG_WHtR)与新发ASCVD之间存在倒“J”型关联(非线性P=0.045;TDAUC=0.640;C=0.634),而结合体质量指数的甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数(TyG_BMI)、结合腰围的甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数(TyG_WC)和结合腰臀比的甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数(TyG_WHR)呈现正向线性关联(趋势性P均<0.05),预测性能次之(C=0.564,0.588,0.598)。尽管TyG和胰岛素抵抗代谢评分(METS-IR)与ASCVD风险增加有关(TyG:Q2 vs. Q1,HR=1.23,Q4 vs. Q1,HR=1.24;METS-IR:非线性P=0.045),但它们对新发ASCVD的预测性能不佳。
结论: 结合肥胖测量参数的TyG是CKM 0-3期人群中预测新发ASCVD的理想IR替代标志物,监测该类指标将有助于CKM人群的心血管疾病防控。
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome; Insulin resistance; Triglyceride-glucose index.
© 2025《四川大学学报(医学版)》编辑部 Copyright ©2025 Journal of Sichuan University (Medical Science Edition).
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突 本文作者赵星是本刊编委会青年编委。该文在编辑评审过程中所有流程严格按照期刊政策进行,且未经其本人经手处理。除此之外,所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triglyceride-glucose-related indices and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in individuals with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome stages 0-3: a prospective cohort study of 282,920 participants in the UK Biobank.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jul 10;24(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02842-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40640813 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of different insulin resistance-related indices with the incidence and progression trajectory of cardiometabolic multimorbidity: a prospective cohort study from UK biobank.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jun 18;24(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02819-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40533754 Free PMC article.
-
Association between insulin resistance indices and outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 22;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02595-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39844150 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose-body mass index and the incidence of cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis of cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 22;24(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02584-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39844258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does diabetes status modify the association between the triglyceride-glucose index and major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary heart disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Aug 4;24(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02890-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40760488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 张 瑾, 孙 妍 中老年人心血管代谢性共病患病率与影响因素的Meta分析. 中国老年保健医学. 2023;21(6):9–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2671.2023.06.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
