Olink proteomics reveals TNFRSF9 as a biomarker for abdominal aortic aneurysms
- PMID: 40599317
- PMCID: PMC12209979
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112828
Olink proteomics reveals TNFRSF9 as a biomarker for abdominal aortic aneurysms
Abstract
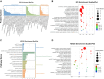
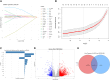
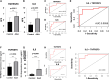
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a serious cardiovascular disease associated with chronic inflammation. The purpose of this study was to use the Olink proteomics to reveal serum inflammatory markers in AAA. We examined the expression levels of 92 inflammation-related proteins in patients with AAA (n = 18) and healthy individuals (n = 10) using the Olink proximity extension assay (PEA) inflammatory plate. Olink proteomics identified 38 differential proteins. Combined analysis of Olink proteomics and GSE183464 showed interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9) were upregulated at both gene and protein levels in AAA patients. The ELISA results were consistent with the Olink proteomics results, and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis revealed that the binding of TNFRSF9 and IL-6 has high diagnostic value (Olink AUC = 0.9056; ELISA AUC = 0.950). Subsequently, elevated TNFRSF9 expression in AAA was confirmed by animal models, suggesting that TNFRSF9 may serve as a potential biomarker for AAA.
Keywords: Cardiovascular medicine; Proteomics.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic surgery for elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 4;5(5):CD012302. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012302.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28471523 Free PMC article.
-
Medical treatment for small abdominal aortic aneurysms.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD009536. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009536.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972146 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular treatment for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 26;5(5):CD005261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005261.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28548204 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological treatment of vascular risk factors for reducing mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 12;1(1):CD010447. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010447.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28079254 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wanhainen A., Van Herzeele I., Bastos Goncalves F., Bellmunt Montoya S., Berard X., Boyle J.R., D'Oria M., Prendes C.F., Karkos C.D., Kazimierczak A., et al. Editor's Choice -- European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2024 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-Iliac Artery Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2024;67:192–331. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2023.11.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kniemeyer H.W., Kessler T., Reber P.U., Ris H.B., Hakki H., Widmer M.K. Treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, a permanent challenge or a waste of resources? Prediction of outcome using a multi-organ-dysfunction score. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2000;19:190–196. doi: 10.1053/ejvs.1999.0980. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

