Biosynthesis of a dual growth factors (GFs) functionalized silk sericin hydrogel to promote chronic wound healing in diabetic mice
- PMID: 40599340
- PMCID: PMC12212160
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.06.017
Biosynthesis of a dual growth factors (GFs) functionalized silk sericin hydrogel to promote chronic wound healing in diabetic mice
Abstract
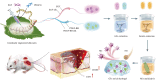
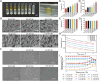
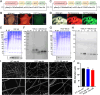
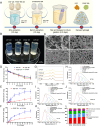
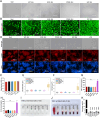
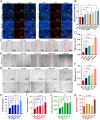
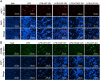
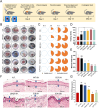
Chronic non-healing wounds, such as diabetic foot, pressure sores and bedsores have seriously affected the life quality of patients worldwide. GFs provide a potential solution to promote chronic wound healing by promoting cell proliferation and differentiation. However, limited resource, high cost, and instability in vivo greatly hindered their clinical applications. In present study, two silk gland bioreactor silkworm stains were generated to successfully synthesize functional silk fibers incorporating high expressions of EGF and PDGF-BB. The two GFs functionalized silk raw materials were used to fabricate a dual GFs sericin hydrogel (E/P-SH) delivering system with tunable material performances for better cell adhesion and biocompatibility, sustainable release of the dual GFs to synergistically promote cell proliferation and migration, which realized the significant healing of chronic full-thickness skin wound in diabetic mice within 12 days with more organized collagen arrangement and better epithelialization degree by reducing inflammatory response and promoting vascularization. These findings demonstrated that the biosynthesized dual GFs-SH delivering system provides an opportunity to broaden the wide utility of GFs in clinical treatment of diabetic wound healing.
Keywords: Biosynthesis; Cell proliferation; Chronic diabetic wound healing; Growth factors; Sericin hydrogels.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibiotics and antiseptics for surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 29;3(3):CD011712. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011712.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27021482 Free PMC article.
-
Topical antimicrobial agents for treating foot ulcers in people with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 14;6(6):CD011038. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011038.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28613416 Free PMC article.
-
Dressings and topical agents for the management of open wounds after surgical treatment for sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013439. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013439.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593897 Free PMC article.
-
Dressings and topical agents for treating pressure ulcers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 22;6(6):CD011947. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011947.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28639707 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of debriding agents in treating surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(14):1-131. doi: 10.3310/hta5140. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11399237
References
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C.N., Mbanya J.C., Pavkov M.E., Ramachandaran A., Wild S.H., James S., Herman W.H., Zhang P., Bommer C., Kuo S., Boyko E.J., Magliano D.J. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Wu Y., Gong H., Xiong Y., Chen Y., Li L., Zhi B., Lv S., Peng T., Zhang H. A multifunctional herb-derived glycopeptide hydrogel for chronic wound healing. Small. 2024 - PubMed
-
- Xiong Y., Feng Q., Lu L., Qiu X., Knoedler S., Panayi A.C., Jiang D., Rinkevich Y., Lin Z., Mi B., Liu G., Zhao Y. Metal-organic frameworks and their composites for chronic wound healing: from bench to bedside. Adv. Mater. 2024;36(2) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

