Phytochemicals, Extraction Methods, Health Benefits, and Applications of Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) and Its By-Products: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 40599359
- PMCID: PMC12209715
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70483
Phytochemicals, Extraction Methods, Health Benefits, and Applications of Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) and Its By-Products: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
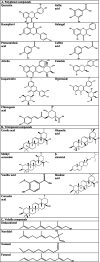
Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica), a plant native to China and having extensive medicinal values, has recently drawn considerable attention. The current research on loquat mainly centers on its preservation, processing, and extraction of bioactive compounds. Nevertheless, there are still challenges and problems in the medical research and application of loquat and its byproducts. This study intends to explore the pros and cons of various methods for extracting abundant bioactive substances from loquat and its byproducts. The crucial antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hypoglycemic roles of these bioactive substances and their significance in the domains of medicine and healthcare were evaluated. A thorough examination of the functions and mechanisms of action of the bioactive compounds in loquat will provide new insights and opportunities for the enhancement of the medicinal potential of loquat. It will also act as an important reference for research and application in related fields.
Keywords: active substances; biological activity; extraction mode; loquat and by‐products; mechanism of action.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ayseli, M. T. , and İpek Ayseli Y.. 2016. “Flavors of the Future: Health Benefits of Flavor Precursors and Volatile Compounds in Plant Foods.” Trends in Food Science & Technology 48: 69–77. 10.1016/j.tifs.2015.11.005. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

