Tailored Extracellular Vesicles from Dental Stem Cells: Advances in Specific Modifications for Enhanced Therapeutic Applications
- PMID: 40599394
- PMCID: PMC12209602
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S528190
Tailored Extracellular Vesicles from Dental Stem Cells: Advances in Specific Modifications for Enhanced Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
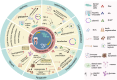
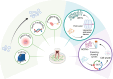
Extracellular vesicles(EVs) derived from dental stem cells have emerged as a key focus in regenerative medicine, owing to their remarkable ability to promote tissue repair and regeneration. Recent advancements revealed that targeted modifications can significantly boost their functional properties, creating new possibilities for the regeneration field. This article provides an overview of the most recent progress in EVs derived from dental stem cells research, with a particular emphasis on diverse engineering strategies such as genetic, chemical, and physical techniques, and their role in enhancing therapeutic performance. Furthermore, the influence of these engineering methods on the yield of EVs is thoroughly examined, offering critical perspectives for improving large-scale manufacturing efficiency. Pretreatment-generated conditioned dental stem cells-derived EVs are also explored as an innovative approach, demonstrating superior biological functions and regenerative potential. By integrating contemporary findings, this review underscores the superior capabilities of modified EVs derived from dental stem cells in driving progress in regenerative medicine and lays the groundwork for future investigations focused on clinical applications and therapeutic innovation.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; hypoxia; inflammation; preconditioning; predifferentiation; regeneration.
© 2025 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from Schwann cells to enhance bone and dental tissue regeneration: a literature review.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 11;23(1):502. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03585-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40646600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Versatility of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in tissue repair and regenerative applications.Biochimie. 2023 Apr;207:33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2022.11.011. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Biochimie. 2023. PMID: 36427681 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Integrated Biomaterials in Bone Tissue Engineering Applications: Current Progress and Future Perspectives.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 17;20:7653-7683. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S522198. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40546799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory properties of naïve and inflammation-informed dental pulp stem cell derived extracellular vesicles.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 19;15:1447536. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447536. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39224602 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic extracellular vesicles derived from human dental pulp stem cells facilitate periodontal tissue regeneration.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jul 11;25(1):1150. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06531-z. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40646544 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

