Comparative Evaluation of a Disinfectant Formulation Comprising Hydrogen Peroxide, Peracetic Acid, and Acetic Acid Against Aspergillus niger, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus on Various Surfaces in Comparison to Other Disinfectants
- PMID: 40599609
- PMCID: PMC12213054
- DOI: 10.1155/ijm/2602317
Comparative Evaluation of a Disinfectant Formulation Comprising Hydrogen Peroxide, Peracetic Acid, and Acetic Acid Against Aspergillus niger, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus on Various Surfaces in Comparison to Other Disinfectants
Abstract
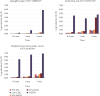
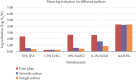
This study investigates the effectiveness of a disinfectant formulation comprising acetic acid, hydrogen peroxide, and peracetic acid (AAHPA) against Aspergillus niger, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus on petri plates, smooth surfaces, and rough surfaces. Comparative analysis with conventional disinfectants such as 70% isopropyl alcohol, 1.5% chlorhexidine gluconate, 10% sodium hypochlorite, and 0.2% hydrogen peroxide reveal AAHPA's superior performance, achieving significantly higher log reduction (p < 0.05) and percentage reduction (p < 0.01) against A. niger in 5 min on petri plates. On smooth and rough surfaces, AAHPA exhibits exceptional efficacy, demonstrating the highest log and percentage reduction against A. niger in 0.5, 1, and 5 min, surpassing other disinfectants. AAHPA shows the highest bacterial decline against E. coli and S. aureus, followed by 0.2% hydrogen peroxide. In some cases, 0.2% hydrogen peroxide was slightly more effective than AAHPA against E. coli and S. aureus in 5 min. Time-dependent analysis of log reduction trends emphasizes AAHPA's rapid and consistent effectiveness, particularly in 0.5 min, positioning it as a promising disinfectant formulation with broad-spectrum efficacy across diverse surfaces.
Copyright © 2025 Md. Raisul Islam Rabby et al. International Journal of Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Singh P., Rani A., Pal S. Comparative Efficacy of Disinfectant Against Routine Lab Bacterial Contaminants. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research . 2014;3(9):709–715.
-
- Wolfe M. K., Gallandat K., Daniels K., Desmarais A. M., Scheinman P., Lantagne D. Handwashing and Ebola Virus Disease Outbreaks: A Randomized Comparison of Soap, Hand Sanitizer, and 0.05% Chlorine Solutions on the Inactivation and Removal of Model Organisms Phi 6 and E. coli From Hands and Persistence in Rinse Water. PLoS One . 2017;12(2) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172734.e0172734 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

