Comparison of Computed Tomography and Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Recurrent Subdiaphragmatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Resection
- PMID: 40599642
- PMCID: PMC12212096
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S524399
Comparison of Computed Tomography and Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Recurrent Subdiaphragmatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Resection
Abstract
Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Although surgical resection and liver transplantation are considered curative, recurrence is common, especially after hepatectomy. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) offers a minimally invasive alternative for treating recurrent HCC. However, its efficacy is influenced by tumor location and imaging guidance. This study aims to compare the outcomes of CT-guided and US-guided RFA in patients with single small recurrent HCCs located in the subdiaphragmatic region after hepatectomy.
Methods: In this retrospective single-center study, we included patients who received RFA for recurrent HCC following curative hepatectomy between 2008 and 2020. Patients were categorized into CT-guided or US-guided RFA groups. RFA was performed by experienced interventional radiologists, and follow-up imaging was conducted every 3-6 months to assess recurrence. The primary outcome was recurrence-free survival (RFS), and the secondary outcome was overall survival (OS).
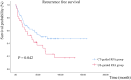
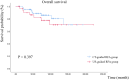
Results: In this study, 59 and 32 patients with subdiaphragmatic lesions underwent CT-guided- and US-guided RFA, respectively, for single recurrent HCC. The CT-guided group showed larger tumor size, lower recurrence rates, and significantly better RFS in Kaplan-Meier analysis compared to the US-guided group (49.5 months vs 35.7 months, p value= 0.042). Multivariate analysis confirmed a superior RFS hazard ratio (HR=0.551) for CT-guided RFA, although the overall survival showed no significant difference. Major complications were absent in both groups.
Conclusion: CT-guided RFA provides improved RFS for subdiaphragmatic recurrent HCC, highlighting its potential as a preferred technique for challenging anatomical locations. Further multicenter prospective studies are necessary to validate these findings and assess the long-term survival outcomes.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; image-guiding; post-operative treatment; radiofrequency ablation; recurrence.
© 2025 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma disclosure form and declare that no support, financial or otherwise, has been received from any organization that may have an interest in the submitted work and that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources