Phase Angle Predicts Malnutrition Risk and 6-month Mortality in Older Patients with Multimorbidity: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 40599689
- PMCID: PMC12209526
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S518795
Phase Angle Predicts Malnutrition Risk and 6-month Mortality in Older Patients with Multimorbidity: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Background: This study examined the utility of the phase angle (PhA) in predicting malnutrition risk and 6-month mortality in older patients with multimorbidity.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of 104 hospitalized older adults with multiple chronic conditions. Data on clinical parameters, body composition, and nutritional status (via Nutritional Risk Screening 2002) were analyzed. Pearson's correlation analysis and receiver operating characteristic analysis were used to identify the optimal PhA cutoff for malnutrition risk. Mortality and malnutrition were compared between the low and high PhA groups.
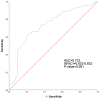
Results: PhA was significantly correlated with age, BMI, hemoglobin, albumin, triglycerides, and the extracellular water/total body water ratio (all P < 0.05). The optimal PhA cutoff was 3.15°, which had 62% sensitivity and 79% specificity for malnutrition prediction. Patients in the low PhA group had significantly higher rates of malnutrition (80.85% vs 40.35%, P < 0.05) and mortality (29.79% vs 3.5%, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: PhA is a clinically valuable tool for assessing malnutrition risk and predicting mortality in older patients with multimorbidity. It enables early identification and intervention, improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: aged; malnutrition; mortality; multiple chronic conditions; phase angle.
© 2025 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Dou LY, Huang J, Zhang ZX, Ye S, Zhang MK. Recent advances in treatment burden of multimorbidity in elderly patients. Chin Gen Pract. 2020;23:874–879. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.621 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical