Advancing open-source visual analytics in digital pathology: A systematic review of tools, trends, and clinical applications
- PMID: 40599690
- PMCID: PMC12210317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpi.2025.100454
Advancing open-source visual analytics in digital pathology: A systematic review of tools, trends, and clinical applications
Abstract
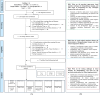
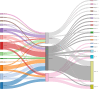
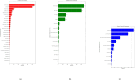
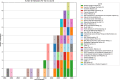
Histopathology is critical for disease diagnosis, and digital pathology has transformed traditional workflows by digitizing slides, enabling remote consultations, and enhancing analysis through computational methods. In this systematic review, we evaluated open-source visual analytics abilities in digital pathology by screening 254 studies and including 52 that met predefined criteria. Our analysis reveals that these solutions-comprising abilities (n = 29), software (n = 13), and frameworks (n = 10)-are predominantly applied in cancer research (e.g., breast, colon, ovarian, and prostate cancers) and primarily utilize whole slide images. Key contributions include advanced image analysis capabilities (as demonstrated by platforms such as QuPath and CellProfiler) and the integration of machine learning for diagnostic support, treatment planning, automated tissue segmentation, and collaborative research. Despite these promising advancements, challenges such as high computational demands, limited external validation, and difficulties integrating into clinical workflows remain. Future research should focus on establishing standardized validation frameworks, aligning with regulatory requirements, and enhancing user-centric designs to promote robust, interoperable solutions for clinical adoption.
Keywords: Cancer research; Clinical implementation; Computational pathology; Digital pathology; Histopathology; Image analysis; Machine learning in pathology; Open-source; Visual analytics; Whole slide imaging.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

