The functional near infrared spectroscopy applications in children with developmental diseases: a review
- PMID: 40599736
- PMCID: PMC12209276
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1495138
The functional near infrared spectroscopy applications in children with developmental diseases: a review
Abstract
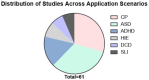
This review provides a comprehensive synthesis of the application of functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) in pediatric developmental disorders, with a particular emphasis on its potential for clinical translation. fNIRS is a portable and non-invasive brain imaging technique that detects the relative concentration changes of oxyhemoglobin (HbO2), deoxyhemoglobin (HbR), and total hemoglobin in the cerebral cortex. These measurements effectively reflect cortical activation, making fNIRS a valuable tool in the field of pediatric neurodevelopmental research. The inherent resistance of fNIRS to interference, coupled with its adaptability to naturalistic settings, renders it particularly well-suited for pediatric populations. In this context, we undertook a meticulous and comprehensive literature search, employing predefined strategies and stringent inclusion/exclusion criteria (which are elaborated upon in the text). Our aim was to identify and review fNIRS studies across a wide range of developmental disorders. These disorders encompass cerebral palsy (CP), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), conditions related to preterm infants, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), and idiopathic language disorders. Our synthesis uncovers distinct hemodynamic patterns associated with specific developmental disorders. For example, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is marked by atypical activation within social brain networks, whereas attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is characterized by diminished activation in the prefrontal cortex. These findings not only shed light on the neurophysiological foundations of these disorders but also highlight the potential of fNIRS as a diagnostic biomarker. This review aims to inform the clinical application of fNIRS by providing a critical evaluation of its mechanistic insights and potential clinical pathways, thereby advancing its role in the diagnosis and management of developmental disorders.
Keywords: children; developmental diseases; functional near infrared spectroscopy; hemodynamics; research progress.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zou, Huang, Wu, Wei, Yin, Chen and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tong Y, Wang Q, Wang X, Xiang Y, Cheng L, Hu X, et al. A scoping review of functional near-infrared spectroscopy biomarkers in late-life depression: depressive symptoms, cognitive functioning, and social functioning. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. (2024) 341:111810. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2024.111810, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous