A DFT study of structural and electronic properties of copper indium ditelluride Cu m-1In m Te2 m-2 with m = 2-5 neutral and anion clusters
- PMID: 40599761
- PMCID: PMC12210369
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra03371c
A DFT study of structural and electronic properties of copper indium ditelluride Cu m-1In m Te2 m-2 with m = 2-5 neutral and anion clusters
Abstract
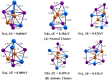
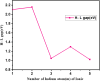
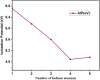
In this work, the electronic and structural properties of Cu m-1In m Te2m-2 neutral and anion clusters are studied. The simulations are carried out using the QUANTUM ESPRESSO/PWSCF package, based on the density functional theory (DFT) principle, which employs a pseudo-potential with a plane wave basis set. Geometry optimization starting from several initial candidate structures was performed for each cluster size to determine the number of possible minimum-energy isomers for each size. The results show that the lowest-energy structures are cubic, ranging from cluster m = 2 to 5, and resemble the chalcopyrite structure. The geometry of neutral and anionic cases exhibits a structural change, including distortion and a transition from two-dimensional to one-dimensional. By considering energetics, i.e. HOMO-LUMO gap, binding energy, ionization potential and electron affinity, the relative stability of Cu m-1In m Te2m-2/(Cu m-1In m Te2m-2)- was measured. From the most stable energy structures, CuIn2Te2/(CuIn2Te2)- were found to have enhanced chemical stability relative to their neighbours. They are a magic-number species. The binding energy and HOMO-LUMO gap of CuIn2Te2/(CuIn2Te2)- clusters show the most significant value, which indicates high chemical stability. The adiabatic ionization potential of the cluster decreases monotonically, showing favor for metallic character as cluster size increases. Both clusters' vertical/adiabatic detachment energies also show a slight odd-even oscillation with an increasing tendency as a function of cluster size. This indicates that the successive increase in metallic atoms results in a decrease in nonmetallic favor. We also analyse the partial charge density of the optimized geometries for both anion and neutral clusters. The numerical value indicates that these clusters, including photovoltaic solar cells and other devices, make a significant contribution to semiconductor design.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Geometric and electronic structures of FeBn-/0/+ clusters (n = 1-3): insights from advanced computational methods.J Mol Model. 2025 Jun 25;31(7):199. doi: 10.1007/s00894-025-06428-2. J Mol Model. 2025. PMID: 40560416
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu L. Li Y. Liu G.-Q. Yu S.-H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024:9832–9873. - PubMed
-
- Islam M. S. Rahman M. K. Hossain M. S. Howlader A. S. Mim J. J. Islam S. Arup M. M. R. Hossain N. Semiconductors. 2024;58:849–873.
-
- Plirdpring T. Kurosaki K. Kosuga A. Day T. Firdosy S. Ravi V. Snyder G. J. Harnwunggmoung A. Sugahara T. Ohishi Y. Adv. Mater. 2012;24:3622–3626. - PubMed
-
- Li S. Li N.-N. Dong X.-Y. Zang S.-Q. Mak T. C. Chem. Rev. 2024;124:7262–7378. - PubMed
-
- Majdoub M. Sengottuvelu D. Nouranian S. Al-Ostaz A. ChemSusChem. 2024;17:e202301462. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

