Interferons and Toxoplasma gondii shape PD-L1 regulation in retinal barrier cells: the critical role of proteases
- PMID: 40599769
- PMCID: PMC12209286
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1607247
Interferons and Toxoplasma gondii shape PD-L1 regulation in retinal barrier cells: the critical role of proteases
Abstract
Introduction: The apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii establishes chronic infection in the central nervous system, including the retina, causing ocular toxoplasmosis (OT). This persistence relies on a fine balance between inflammatory and immunomodulatory mechanisms, especially in the immune-privileged ocular environment. We previously described the immunologic interactions between retinal cells, and particularly the roles of type I and III interferons. In this study, we investigated the regulatory dynamics of PD-L1, a central immunomodulatory receptor on immune cells.
Methods: We first investigated the mechanisms of PD-L1 regulation and the roles of type I and III interferons in an in vitro T. gondii infection model using mono- and co-culture systems of human microglia, astrocytes, and Müller cells. We also assessed PD-L1 expression in an outer blood-retina barrier model (oBRB) of differentiated retinal pigmented epithelial (RPE) cells. Additionally, we looked at retinal cell activation, PD-L1 expression and the roles of these interferons in a mouse model of OT.
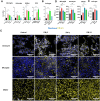
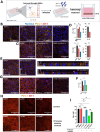
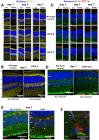
Results: Our findings reveal new roles for type I and III interferons in regulating glial cell activation and PD-L1 expression in RPE, Müller, astrocytes and microglial cells. Notably, Müller cells, the most abundant glial cells in the retina, showed the highest baseline PD-L1 expression at both the mRNA and protein levels, and responded robustly to interferon stimulation. This points to a more prominent immunoregulatory role for Müller cells in the retina than previously recognized. Furthermore, we identified a parasite protease-dependent mechanism that reduces PD-L1 expression in our in vitro oBRB model potentially contributing to immune evasion and inflammation during OT. Finally, in a murine model of OT, we demonstrated that PD-L1 expression reached its peak on day 7 post-infection and that interferon neutralization plays a crucial role in regulating both PD-L1 expression and glial activation.
Discussion: The parasite T. gondii orchestrates the IFN type I and III dependent retinal immune interaction and downregulates PD-L1 in the oBRB by a protease-dependent mechanism, potentially contributing to immune evasion and inflammation in retinal infection. Our results can pave the way to fully elucidate retinal immune networks and PD-L1 regulation mechanisms, offering potential targets for therapeutic interventions in OT and other retinal inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: PD-L1; Toxoplasma gondii; immune privilege; interferons; ocular toxoplasmosis; retina.
Copyright © 2025 Geiller, Cevallos, Tsybenko, Arnoux, Felder-Schmittbuhl and Pfaff.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toxoplasma gondii parasites induce a localized myeloid cell immune response surrounding parasites in the brain during acute infection.mBio. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):e0081025. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00810-25. Epub 2025 Jun 10. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40492741 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii impairs CX3CL1/fractalkine shedding from mouse cortical neurons, leading to microglia activation.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 13:e0107425. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01074-25. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40801546
-
Single cell analysis reveals the roles and regulatory mechanisms of type-I interferons in Parkinson's disease.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Apr 2;22(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01590-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38566100 Free PMC article.
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Active body surface warming systems for preventing complications caused by inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 21;4(4):CD009016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009016.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27098439 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

