Thymosin alpha 1 alleviates inflammation and prevents infection in patients with severe acute pancreatitis through immune regulation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40599771
- PMCID: PMC12208829
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1571456
Thymosin alpha 1 alleviates inflammation and prevents infection in patients with severe acute pancreatitis through immune regulation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Immune and inflammatory disorders are part of the complex pathophysiological processes that exacerbate severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) and subsequent infection. Thymosin alpha 1 (Tα1) is an important immunomodulatory agent in clinical practice, but there is a lack evidence to prove its effectiveness in improving the condition of SAP patients. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy in meta-analysis.
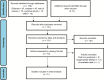
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) up to February 1, 2025. Randomized controlled studies comparing the efficacy of Tα1 as intervention measure with non-Tα1 in improving immune regulation for patients with SAP were included. Review Manager 5.3 was used to assess endpoints in the meta-analysis.
Results: Five randomized controlled trials comprising 706 patients with SAP were included. The results indicated that Tα1 could increase the percentages of CD4+ cells (MD=4.53, 95%CI [3.02, 6.04], P<0.00001) and improve the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (MD=0.42, 95%CI [0.26, 0.58], P<0.00001) in SAP patients. There was no statistically significant decrease in CD8+ cells. For inflammation, lower-dose Tα1 could significantly reduce C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (mg/L) (MD=-30.12, 95%CI [-35.75, -24.49], P<0.00001), while higher-dose Tα1 showed no statistically significant difference (MD=-3.83, 95%CI [-12.14, 4.49], P=0.37). In terms of infection, the immunomodulatory therapy of Tα1 obviously reduced the overall incidence of extrapancreatic infections in SAP patients (RR=0.56, 95%CI [0.40, 0.78], P=0.0005), especially for blood (RR=0.60, 95%CI [0.38, 0.94], P=0.03) and abdominal (RR=0.38, 95%CI [0.19, 0.78], P<0.0001), while the reduction in lung infections was not statistically significant. Regarding hospital stay (days), Tα1 did not significantly reduce the time spent (MD=-4.22, 95%CI [-11.53, 3.10], P=0.26). However, Tα1 reduced the APACHE II score (MD=-1.52, 95%CI [-2.22, -0.83], P<0.0001).
Conclusion: Tα1 can regulate the balance of immune cells and alleviate immune suppression in SAP patients, including increasing CD4+ T cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratios. Tα1 may exert anti-inflammatory and extrapancreatic infection-preventive effects on SAP patients and improve their condition or prognosis. More researches are needed to validate the results.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero, identifier CRD42024570517.
Keywords: immune regulation; infection; inflammation; meta-analysis; severe acute pancreatitis; thymosin alpha 1.
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Yao, Ma, Zhang, Zhou, Xie and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



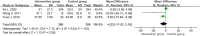
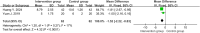
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Enteral nutrition formulations for acute pancreatitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 23;2015(3):CD010605. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010605.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25803695 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing weight gain after smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD006219. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006219.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 6;10:CD006219. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006219.pub4. PMID: 22258966 Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Xie X, Fei S. Research progress on the etiology of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis. Int J Surg. (2020) 47:342–6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115396-20191216-00234 - DOI
-
- Kusiak AA, Jakubowska MA, Stopa KB, Zhang X, Huang W, Gerasimenko JV, et al. Activation of pancreatic stellate cells attenuates intracellular Ca(2+) signals due to downregulation of TRPA1 and protects against cell death induced by alcohol metabolites. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:744. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05186-w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

