Neutrophil ratio trajectory and the short-term outcome of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- PMID: 40599894
- PMCID: PMC12209201
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2025.1555981
Neutrophil ratio trajectory and the short-term outcome of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Abstract
Background: Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is a disease of high mortality and morbidity. The neutrophil ratio (NR), a key indicator, is widely used in clinical practice. However, the relationship between dynamically changing NR and the short-term prognosis of HIE is unclear. We aimed to explore the dynamic changes and potential classifications of NR over time using trajectory analysis and to investigate its relationship with the short-term prognosis of HIE.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of medical records from patients at Shandong University Affiliated Children's Hospital from 2014 to 2022. NR trajectories were modeled in 605 HIE infants using latent growth mixture modeling from 0 to 4 weeks. Then using logistic regression analyze the relationship between NR trajectories and the short-term outcome of HIE. Finally, restricted cubic spline regression model were used to assess the nonlinear relationship between baseline NR and the outcome.
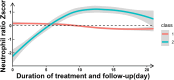
Results: Two distinct NR trajectories could be modeled, a descending (class 1) and a ascending group (class 2). The ascending group (class 2) was associated with the poor outcome (OR 5.72, 95% CI 2.97-10.87, P < 0.001; ORadj 4.78, 95% CI 2.42-9.28, P < 0.001). A significant nonlinear relationship between NR and the risk of poor outcomes (F = 13.16, P < 0.001), potentially exhibiting a U-shaped relationship.
Conclusion: The ascending NR group was strongly associated with poorer short-term outcomes. And both low and high NRs at baseline were associated with increased risk of poorer short-term outcomes.
Keywords: neutrophil ratio; nonlinear; perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; short-term outcome; trajectory analysis.
© 2025 Li, Lang, Deng, Zhou, Kang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dhillon SK, Wassink G, Lear CA, Davidson JO, Holford NHG, Gunn AJ, et al. The effect of size, maturation, global asphyxia, cerebral ischemia, and therapeutic hypothermia on the pharmacokinetics of high-dose recombinant erythropoietin in fetal sheep. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(9):3042. 10.3390/ijms21093042 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources