RmCP, a cerato-platanin protein from Rigidoporus microporus, induces defense responses during interaction with Hevea brasiliensis
- PMID: 40600135
- PMCID: PMC12209261
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1553350
RmCP, a cerato-platanin protein from Rigidoporus microporus, induces defense responses during interaction with Hevea brasiliensis
Abstract
Introduction: The rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) is susceptible to various fungal pathogens with Rigidoporus microporus being one of the most harmful. This fungus causes white root disease in rubber trees which can potentially lead to massive tree losses if left untreated. The use of elicitor proteins in enhancing host plant resistance represents a sustainable approach for disease control by reducing the use of chemical fungicides. Although cerato-platanin proteins (CPs) are recognized elicitors in many pathosystems, CP from R. microporus has not been functionally characterized, leaving its role in rubber-pathogen interactions unknown.
Methods: The coding sequence of the CP homolog RmCP was heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli and purified to homogeneity by two-steps purification method, namely, affinity and size-exclusion chromatography. Bioactivity was assessed by infiltrating micromolar concentrations of RmCP into leaves of the host (H. brasiliensis) and a model non-host (Nicotiana tabacum).
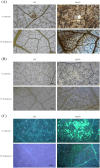
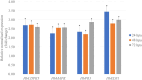
Results: Cell death (Trypan blue), reactive-oxygen species (DAB/NBT), callose deposition (aniline blue) and transcription of four defense-related genes (HbCDPK5, HbMAPK, HbPR3, HbEDS1) were monitored over 72 h. Purified RmCP migrated as a single band between 11 and 17 kDa band. Infiltration induced localized necrosis in N. tabacum within 48 h and in detached rubber leaves within 72 h. Both hosts accumulated H₂O₂ and O₂-, and deposited callose. Additionally, significant up-regulation of HbCDPK5 and HbMAPK (early signaling), followed by strong induction of downstream effector genes, HbPR3 and HbEDS1 was observed in H. brasiliensis. These findings identify RmCP as the first basidiomycete CP shown to activate multilayer innate immunity in a latex-producing perennial.
Conclusion: The study extends the functional spectrum of the CP family beyond ascomycete models and provides a biochemically defined platform for developing protein-based priming agents to combat white-root disease in rubber plantations.
Keywords: Hevea brasiliensis; Rigidoporus microporus; cerato-platanin; elicitor; plant immunity; white root disease.
Copyright © 2025 Maiden, Atan and Mui-Yun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genomic diversity of Capillovirus uniheveae (Betaflexiviridae) infecting Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg. in Hainan, China.BMC Genomics. 2025 Feb 12;26(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11305-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39939933 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher's disease: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Jul;10(24):iii-iv, ix-136. doi: 10.3310/hta10240. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16796930
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
References
-
- Amerik A. Y., Martirosyan Y. T., Martirosyan L. Y., Goldberg V. M., Uteulin K. R., Varfolomeev S. D. (2021). Molecular genetic analysis of natural rubber biosynthesis. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 68, 31–45. doi: 10.1134/S1021443721010039 - DOI
-
- Ashwin N. M. R., Barnabas L., Ramesh Sundar A., Malathi P., Viswanathan R., Masi A., et al. (2017). Comparative secretome analysis of Colletotrichum falcatum identifies a cerato-platanin protein (EPL1) as a potential pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) inducing systemic resistance in sugarcane. J. Proteome 169, 2–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.05.020, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baccelli I., Gonthier P., Bernardi R. (2015). Gene expression analyses reveal a relationship between conidiation and cerato-platanin in homokaryotic and heterokaryotic strains of the fungal plant pathogen Heterobasidion irregulare. Mycol. Prog. 14, 1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11557-015-1063-x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

